Transformation Cont
对应GAMES101 Lecture 04
3D transformations[上一节]
3D变换
缩放(Scale)
平移(Translation)
旋转绕轴[Rotation around x-, y-, or z-axis]
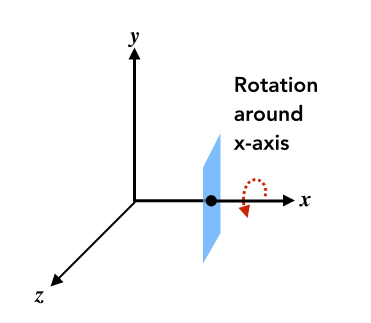
3D Rotations
Compose any 3D rotation from
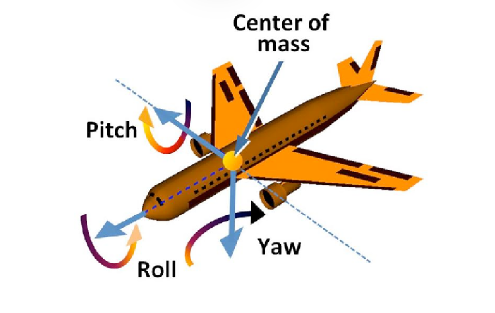
- 欧拉角 (So-called Euler angles)
- 常用于飞行模拟器:滚转,俯仰,偏航 (Often used in flight simulators: roll, pitch, yaw)
Rodrigues’ Rotation Formula
Rotation by angle α around axis n
证明: 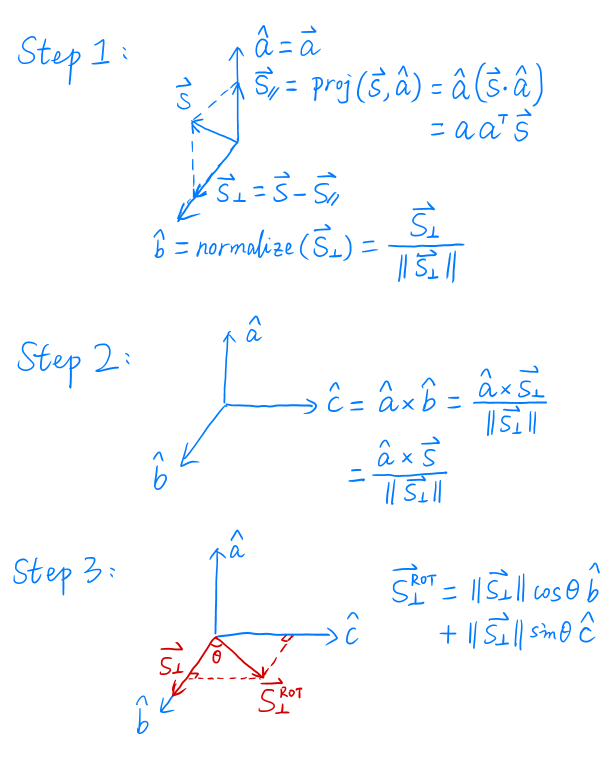
Viewing(观测) transformation
- View(视图)/Camera transformation
- Projection(投影) transformation
- Orthographic(正交) projection
- Perspective(透视) projection
视图/相机变换 (View/Camera transformation)
什么是观测变换? (What is view transformation?)
怎么实现? (How to perform view transformation?)
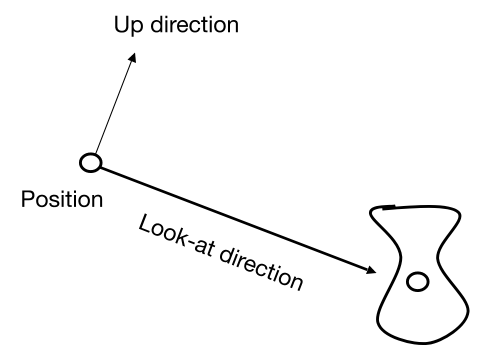
首先定义相机 (Define the camera first)
- 位置 (Position)
- 朝向 (Look-at / gaze direction)
- 上方向(假设垂直于朝向) (Up direction(assuming perp. to look-at))
- 位置 (Position)
关键 (Key observation)
- 同时变换相对不变 (If the camera and all objects move together, the “photo” will be the same)
约定 (How about that we always transform the camera to)
- 位于原点, Up在Y轴, 看向-Z轴 (The origin, up at Y, look at -Z)
- 和相机一起变换物体 (And transform the objects along with the camera)

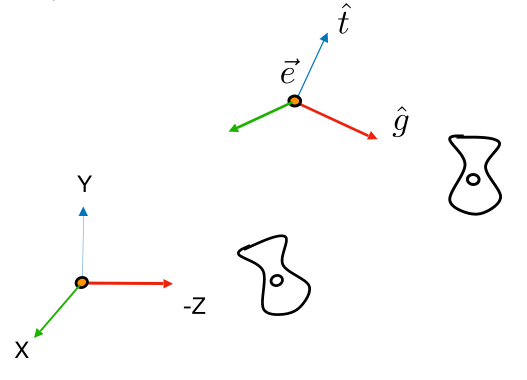
变换相机通过矩阵M (Transform the camera by
) - 位于原点,在Y上,看-Z (So it’s located at the origin, up at Y, look at -Z )
数学上矩阵M (
in math?) - 移动e到原点 (Translates e to origin)
- 旋转g到-Z (Rotates g to -Z)
- 旋转t到Y (Rotates t to Y)
- 旋转(g叉乘t)到X (Rotates (g x t) To X)
- 求最终矩阵
- 步骤一 (Translate e to origin)
- 步骤二 (Rotate g to -Z, t to Y, (g x t) To X)
- 考虑逆旋转 (Consider its inverse rotation: X to (g x t), Y to t, Z to -g)
WHY? 利用逆矩阵的性质,先算从原点到任意点再转置过来
- 总结
- 与相机一起变换物体 (Transform objects together with the camera)
- 直到相机在原点,在Y上,看-Z (Until camera’s at the origin, up at Y, look at -Z)
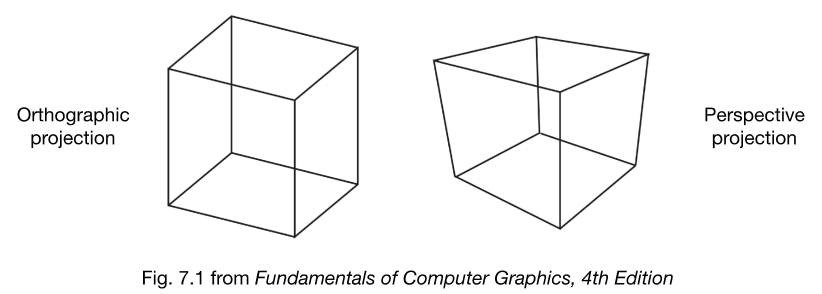
投影变换 (Projection Transformation)
- 计算机图形学中的投影 (Projection in Computer Graphics)
- 3D to 2D
- 正交投影 (Orthographic projection)
- 透视投影 (Perspective projection)
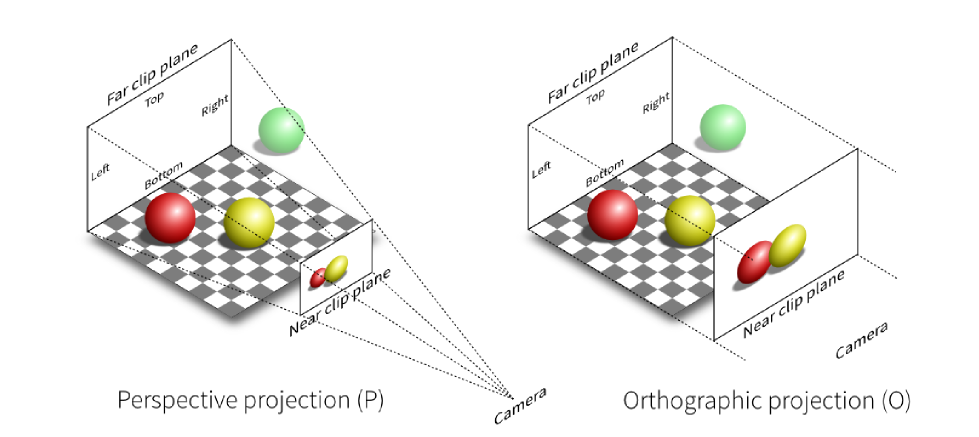
正交投影 (Orthographic Projection)
简单理解
- 相机位于原点,看着-Z,向上看Y
- 去掉Z轴
- 将得到的矩形平移并缩放为[- 1,1]² (Translate and scale the resulting rectangle to [-1, 1]²)
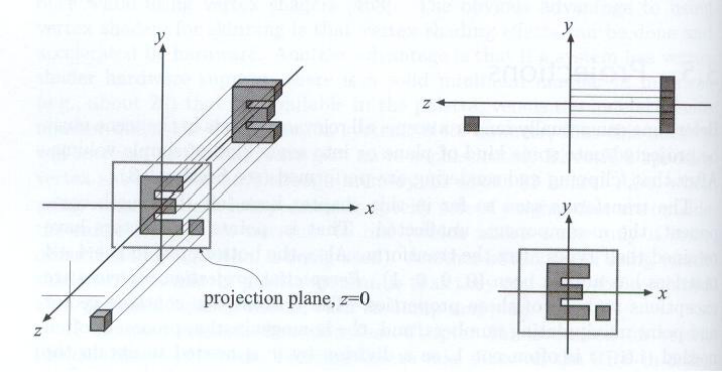
通常来说 (In general)
- We want to map a cuboid [l, r] x [b, t] x [f, n] to the “canonical (正则、规范、标准)” cube [-1, 1]³
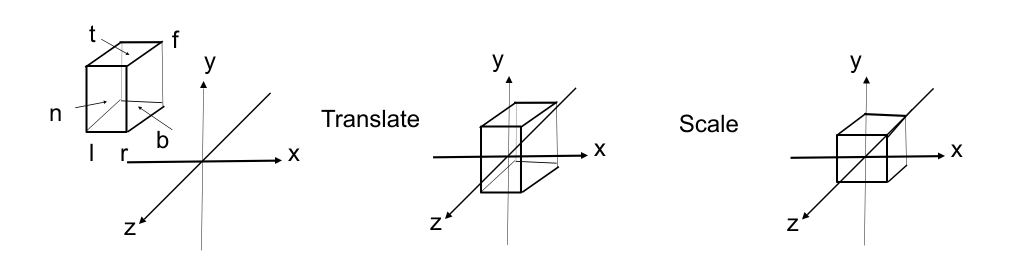
Slightly different orders (to the “simple way”)
- Center cuboid by translating
- Scale into “canonical” cube
平移矩阵(Transformation matrix)
- Translate (center to origin) first, then scale (length/width/height to 2)
Caveat
- Looking at / along -Z is making near and far not intuitive (n > f)
- FYI: that’s why OpenGL (a Graphics API) uses left hand coords
透视投影 (Perspective Projection)
最常见于计算机图形学、美术、视觉系统, 进大远小, 更符合人眼观测
开始之前, 回想一下齐次坐标的性质
- (x, y, z, 1), (kx, ky, kz, k != 0), (xz, yz, z², z != 0) all represent the same point (x, y, z) in 3D
- e.g. (1, 0, 0, 1) and (2, 0, 0, 2) both represent (1, 0, 0)
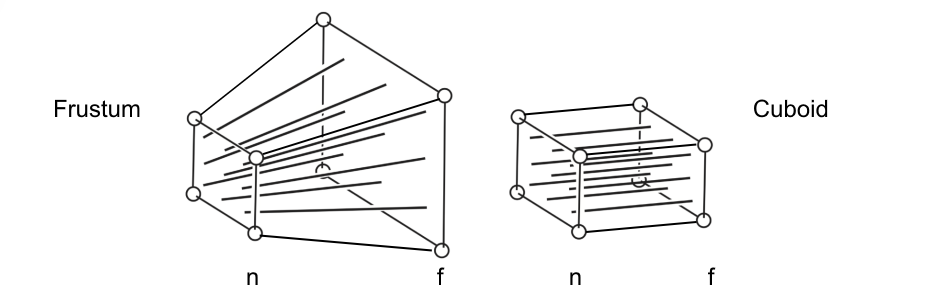
怎么做(How to do perspective projection)
- 首先把截锥体压成一个长方体 (First “squish” the frustum into a cuboid[n->n, f->f][
]) - 做正交投影 (Do orthographic projection[
, already known!])
找对应点之间的关系
Find the relationship between transformed points (x’, y’, z’) and the original points (x, y, z) 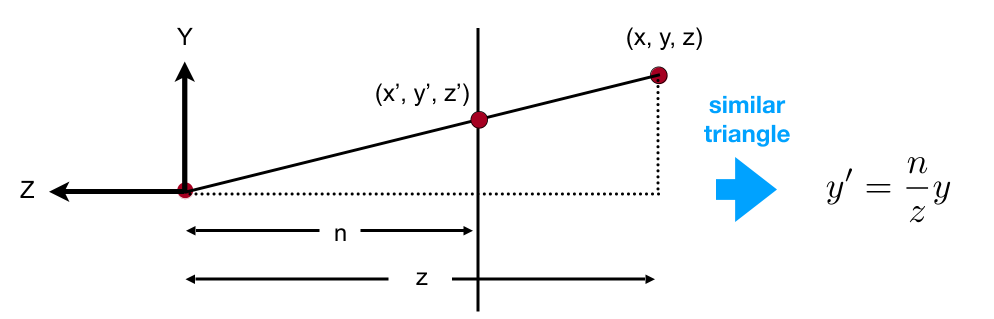
- 齐次坐标系下 (In homogeneous coordinates)
- So the “squish” (persp to ortho) projection does this
- Already good enough to figure out part of
- 求第三行
- Observation: the third row is responsible for z’
- So the third row must be of the form (0 0 A B)
- 最后再做一次正交投影
结尾
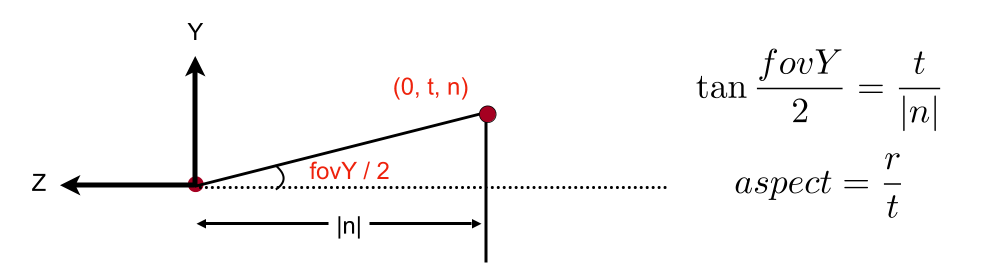
- What’s near plane’s l, r, b, t then?
- If explicitly specified, good
- Sometimes people prefer: vertical field-of-view (fovY) and aspect ratio(assume symmetry i.e. l = -r, b = -t)
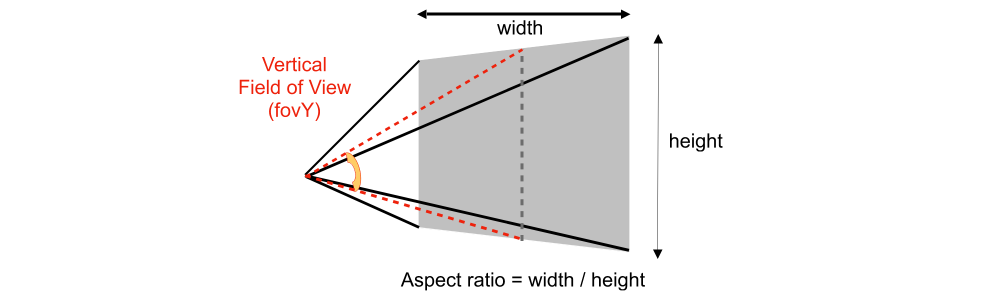
- How to convert from fovY and aspect to l, r, b, t?