光栅化(Rasterization Cont)
关于
Antialiasing and Z-Buffering (反走样(抗锯齿)和深度缓冲)
锯齿的学名:走样
- Antialiasing (反走样)
- Sampling theory (采样理论)
- Antialiasing in practice (实践中的反走样 )
- Visibility / occlusion (可见性/遮挡)
- Z-buffering
Sampling Artifacts (Errors / Mistakes / Inaccuracies) in Computer Graphics (采样时会出现的问题)
Artifacts due to sampling - “Aliasing” (采样产生的伪影——“混叠”)
Jaggies (Staircase Pattern) 锯齿(楼梯形状)
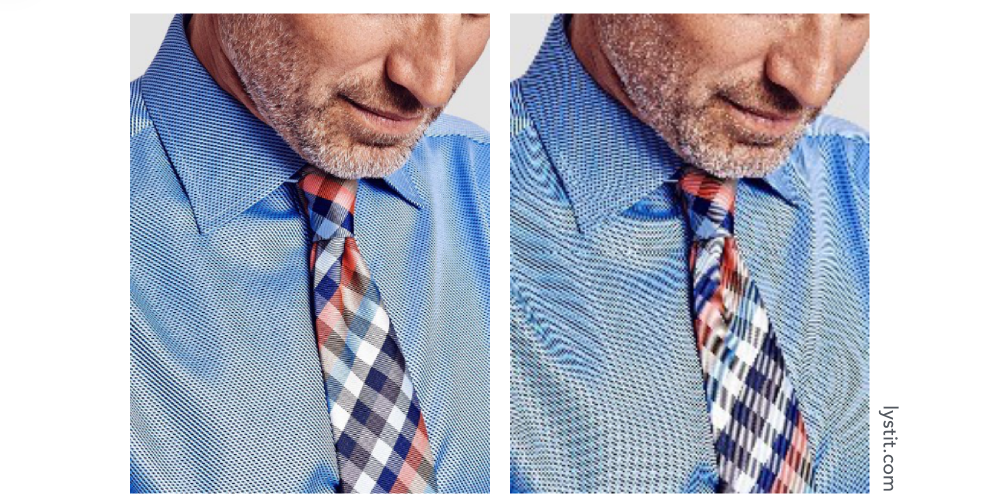
Moiré Patterns in Imaging (摩尔纹)
Skip odd rows and columns (跳过奇数行和奇数列)

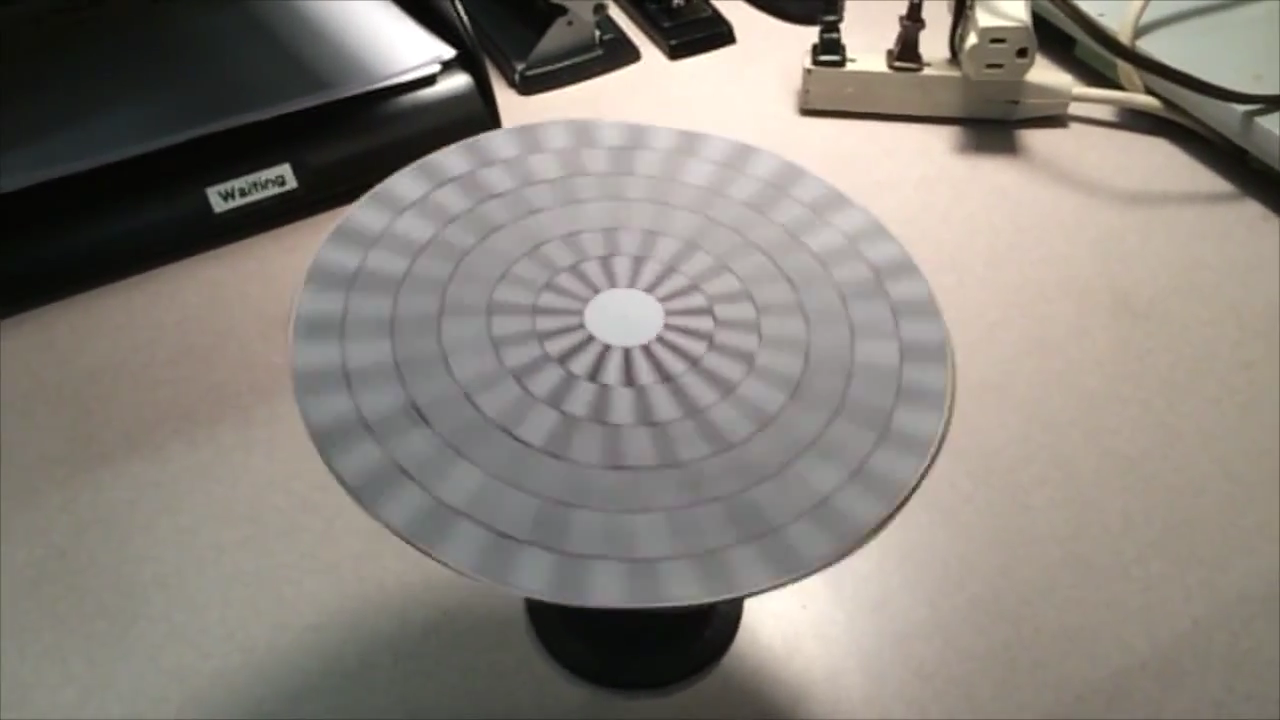
- Wagon Wheel Illusion (False Motion) (车轮错觉(假动作))
人眼在时间上的采样跟不上运动的速度

- [Many more]...
Behind the Aliasing Artifacts (原因)
- Signals are changing too fast (high frequency), but sampled too slowly (信号变化太快(高频)但采样太慢)
Antialiasing (抗锯齿)
Antialiasing Idea: Blurring (Pre-Filtering) Before Sampling (抗锯齿方法: 采样之前做模糊(预滤波))
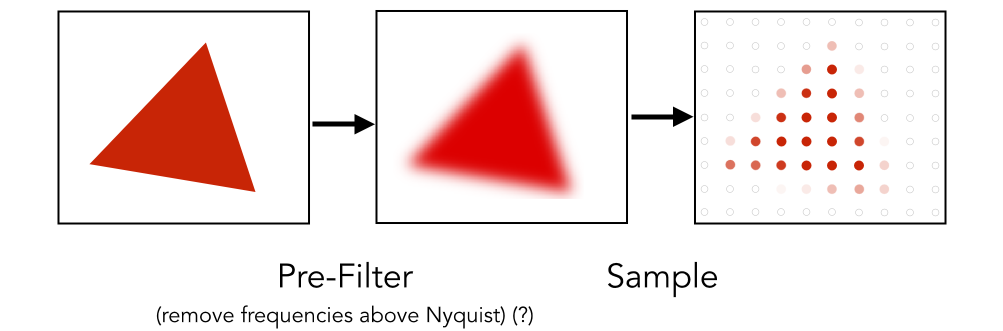
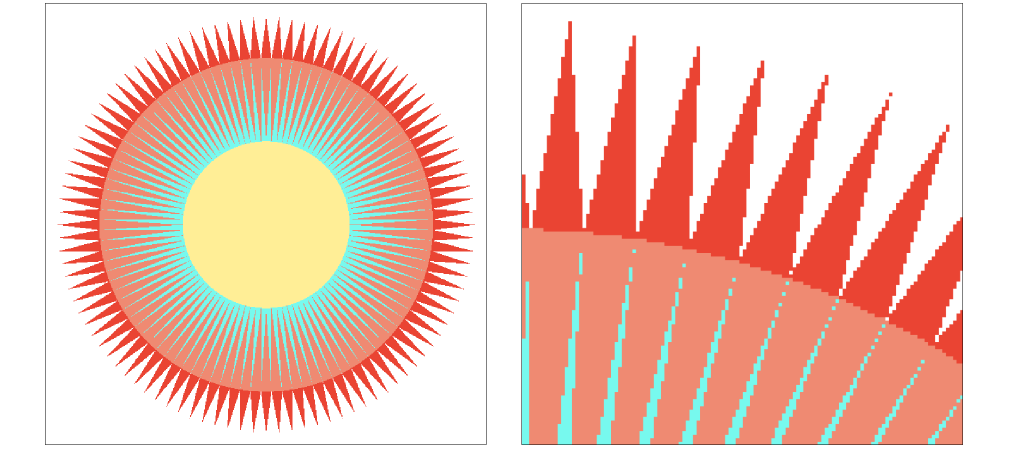
Point Sampling vs Antialiasing (点采样 vs 抗锯齿)
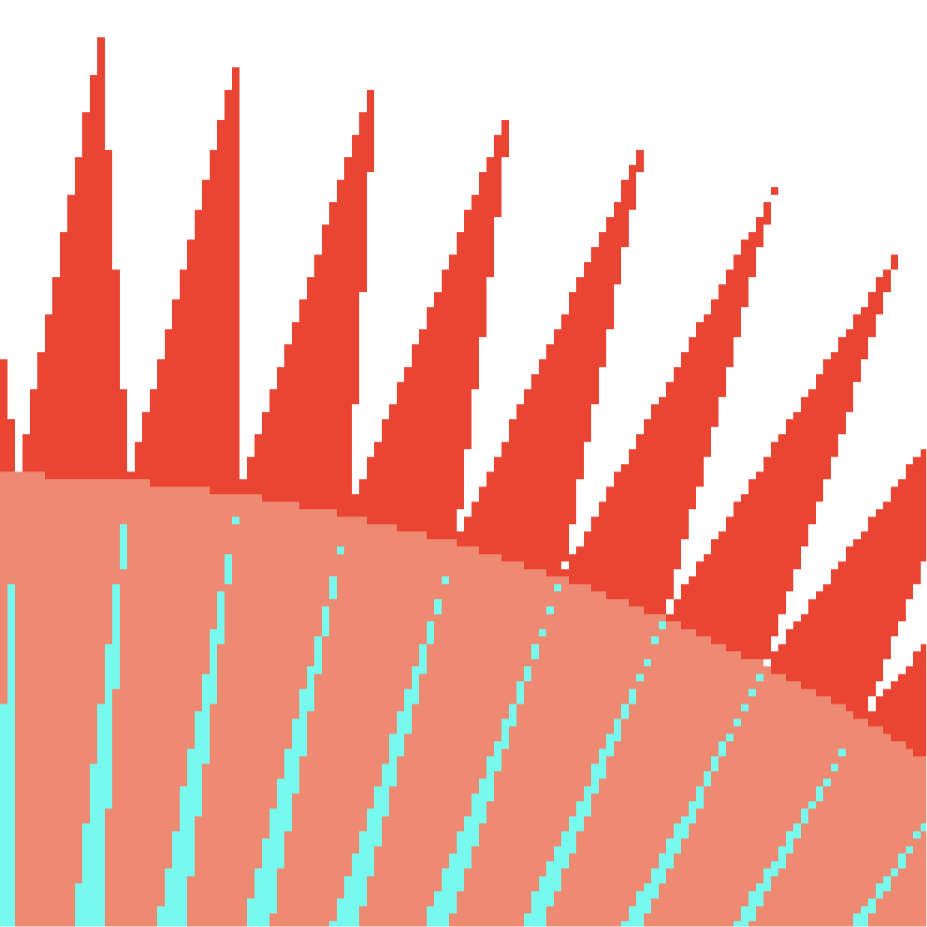
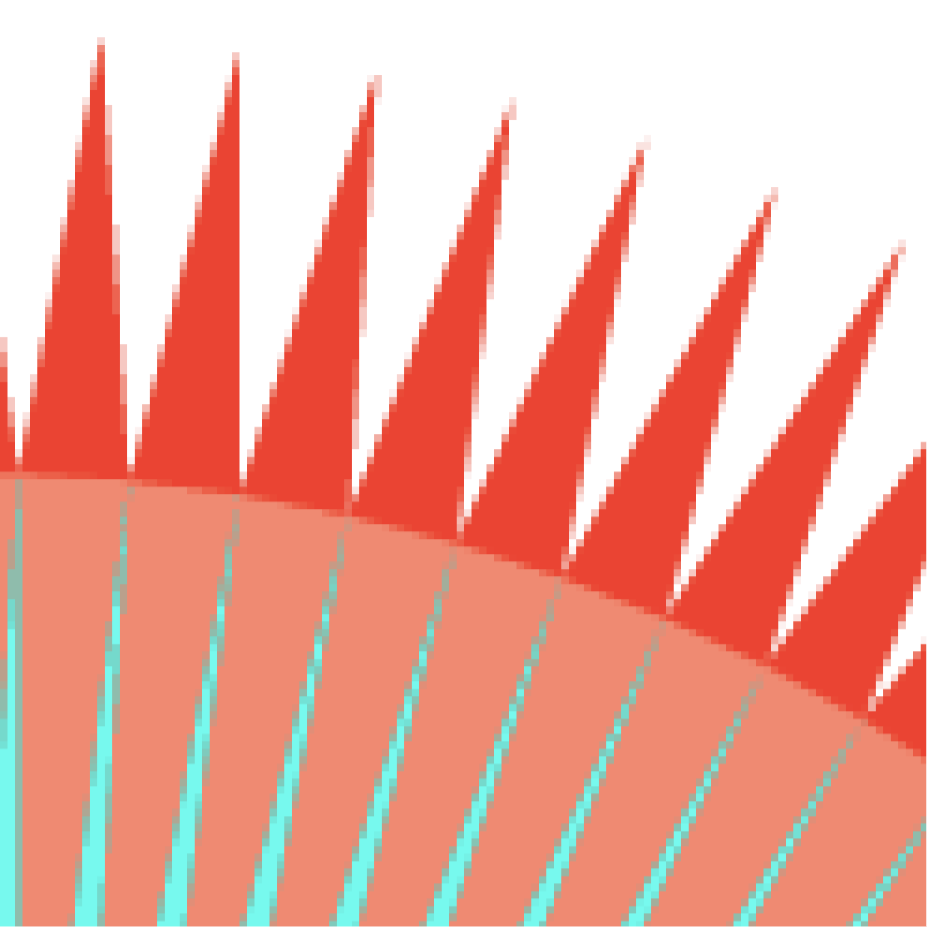
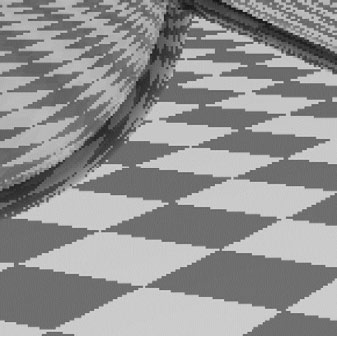
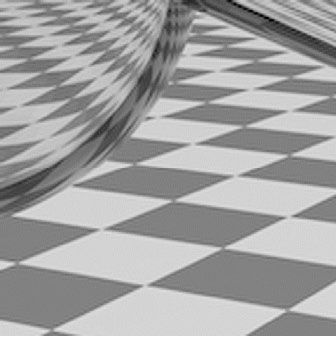
Antialiasing vs Blurred Aliasing
Sample then filter, WRONG!
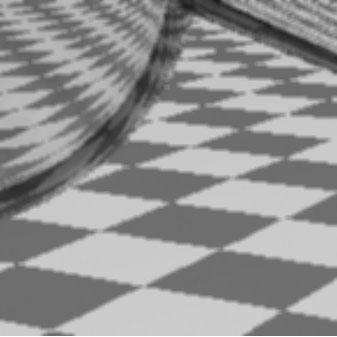

But Why?
- Why undersampling introduces aliasing?
- Why pre-filtering then sampling can do antialiasing?
Let’s dig into fundamental reasons And look at how to implement antialiased rasterization
Frequency Domain (频域)
Sines and Cosines
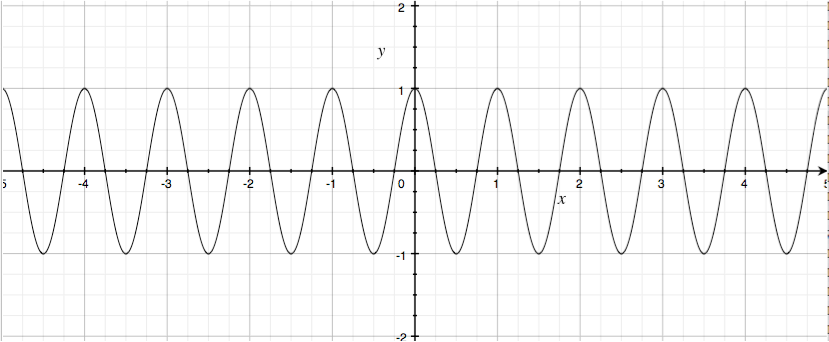
Frequencies (频率)

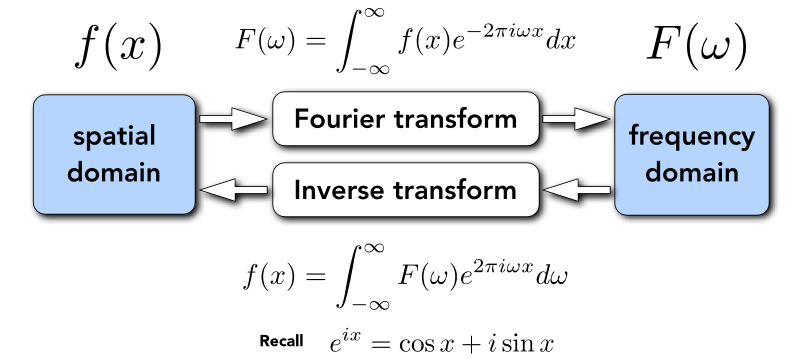
Fourier Transform (傅里叶变换)
Fourier Transform (傅里叶变换)
- Represent a function as a weighted sum of sines and cosines (将函数表示为正弦和余弦的加权和)
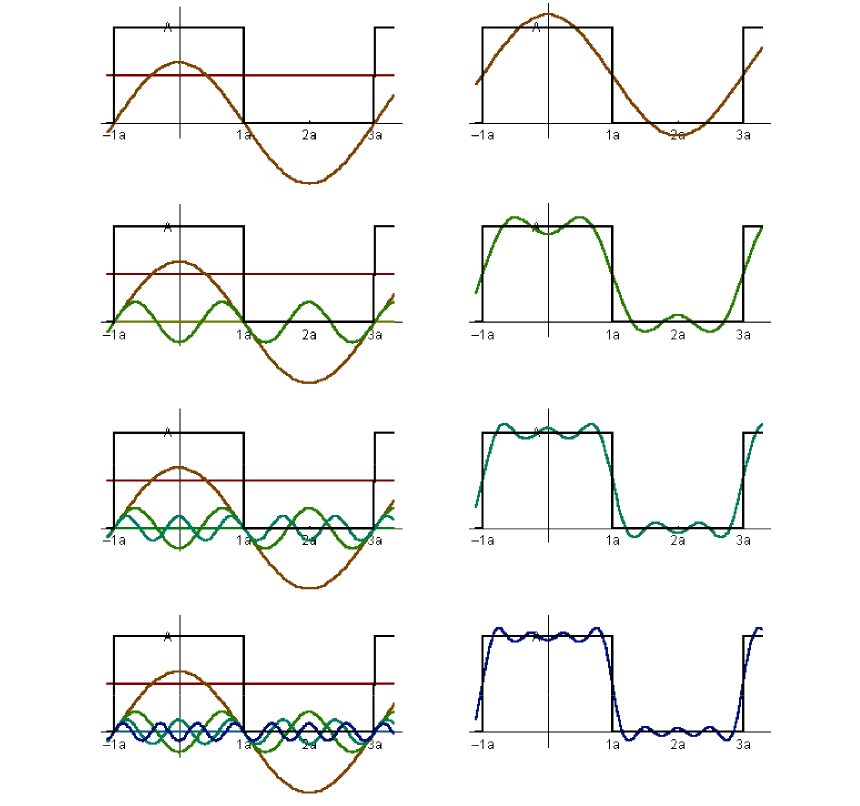
- Fourier Transform Decomposes A Signal Into Frequencies (傅里叶变换会将时域转化为频域)
- Higher Frequencies Need Faster Sampling (更高的频率需要更快的采样)
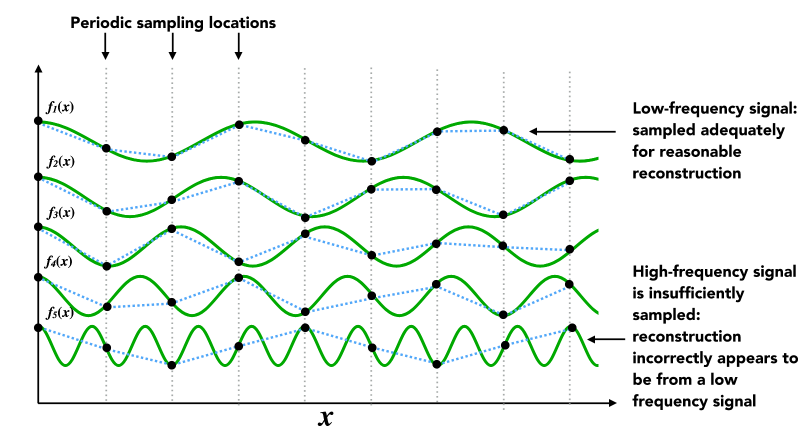
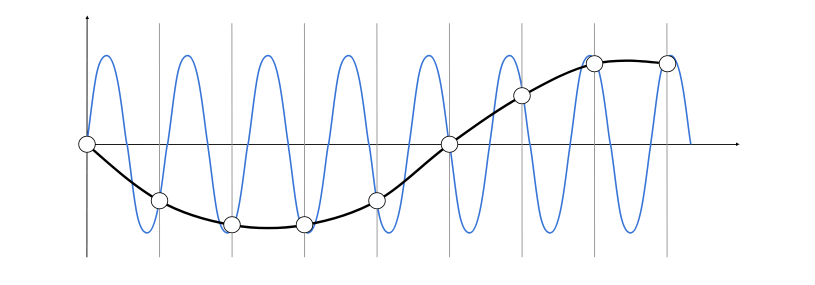
- Undersampling Creates Frequency Aliases
- High-frequency signal is insufficiently sampled: samples erroneously appear to be from a low-frequency signal (高频信号采样不足:采样错误地显示为来自低频信号)
- Two frequencies that are indistinguishable at a given sampling rate are called “aliases” (在给定采样率下无法区分的两个频率称为“别名”)
Filtering (滤波)
Filtering (滤波)
Filtering = Getting rid of certain frequency contents (过滤= 摆脱某些频率内容)
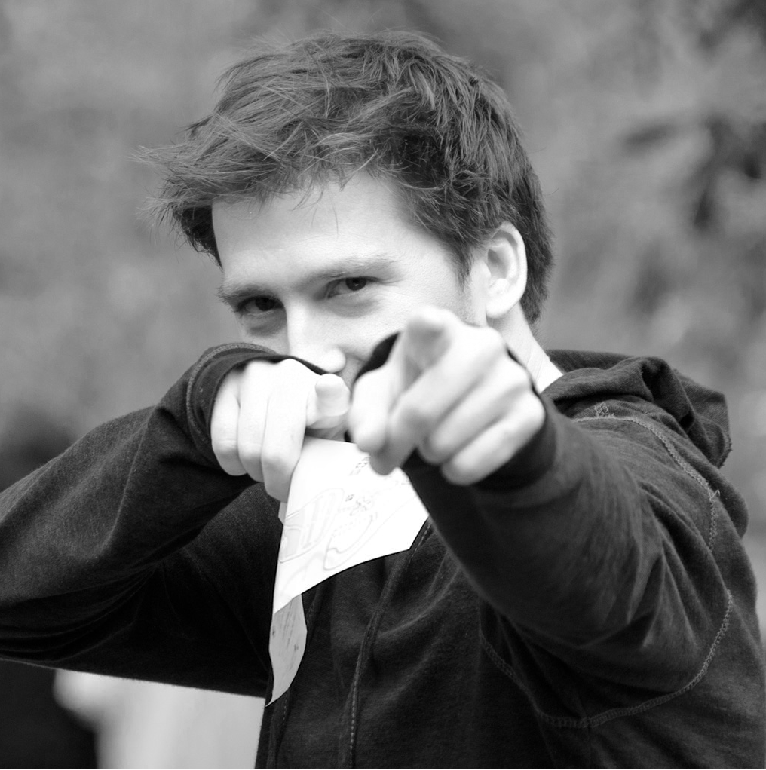
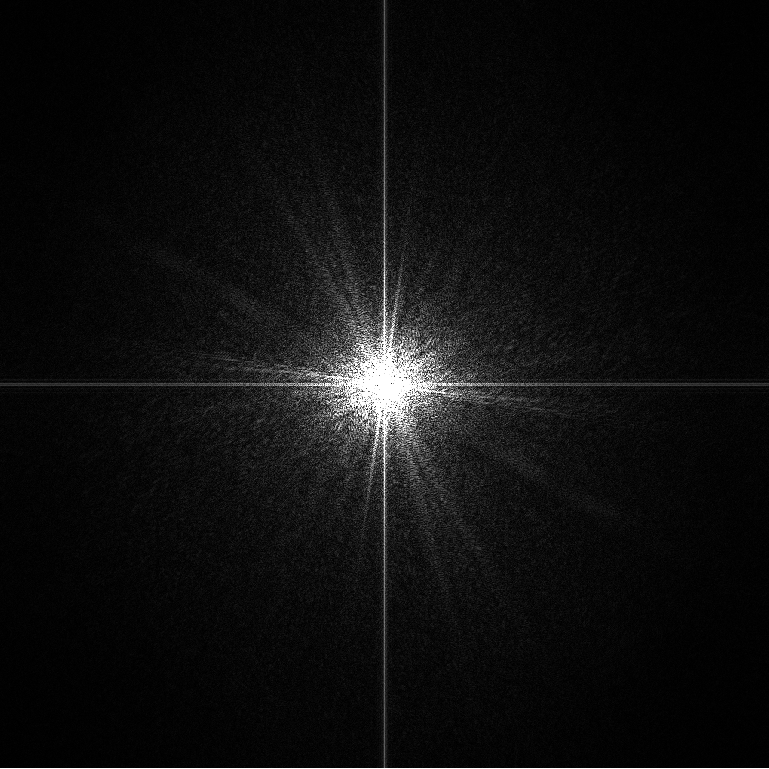
- Visualizing Image Frequency Content (可视化图像频率内容)


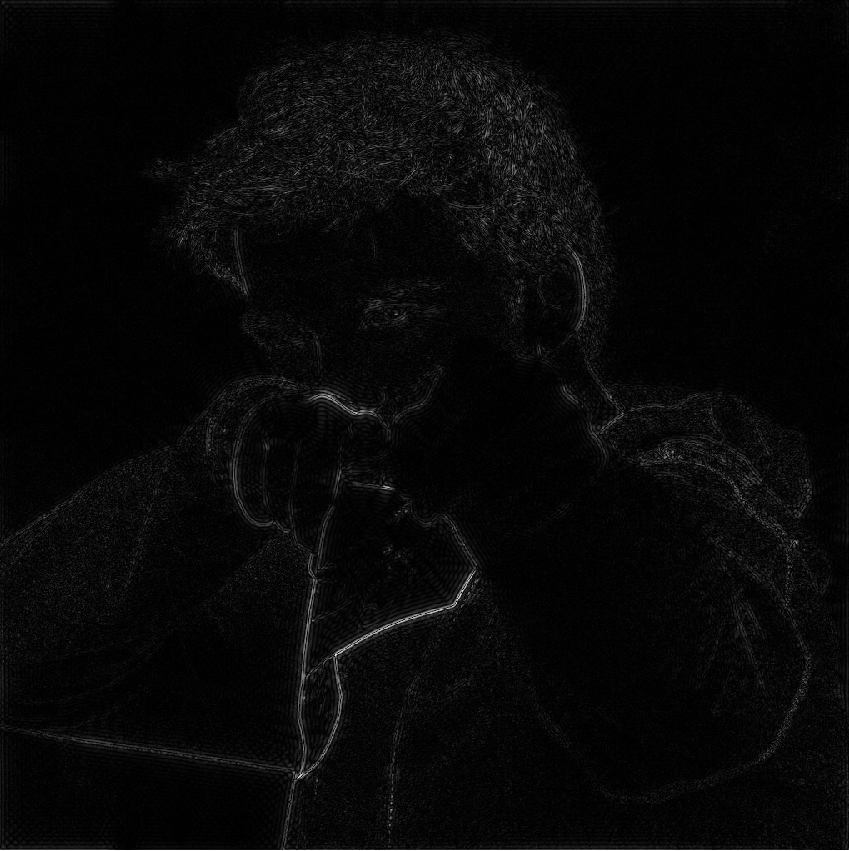
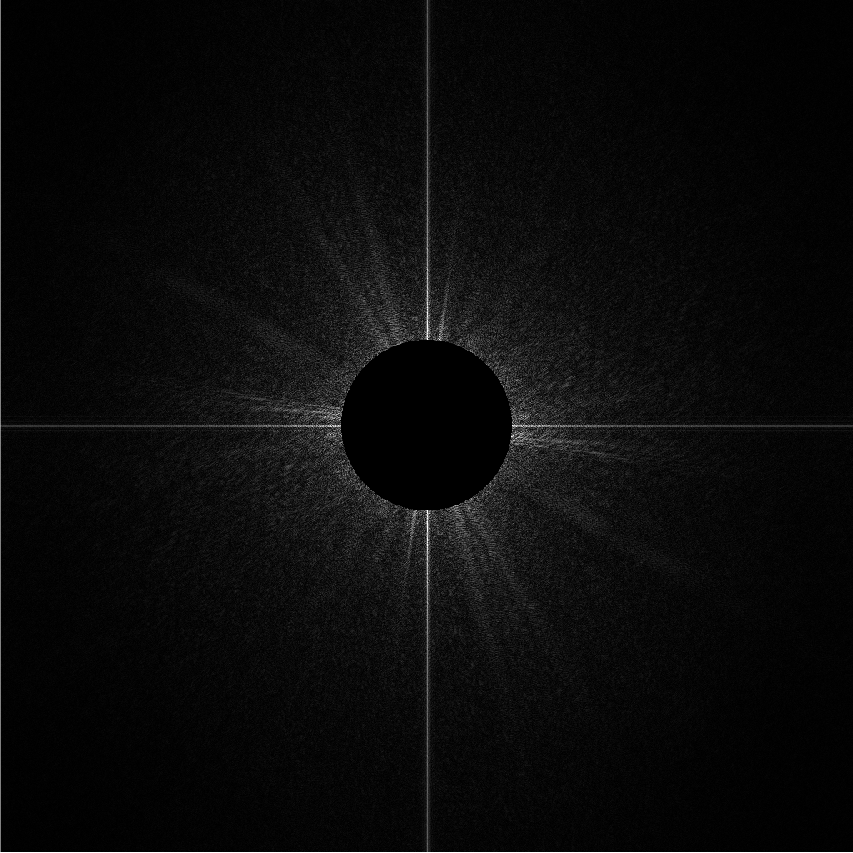
Filter Out Low Frequencies Only (Edges) (滤除低频(边缘))
高通滤波: 只显示高频信息(只显示边界-锐化,将低频信息盖住)


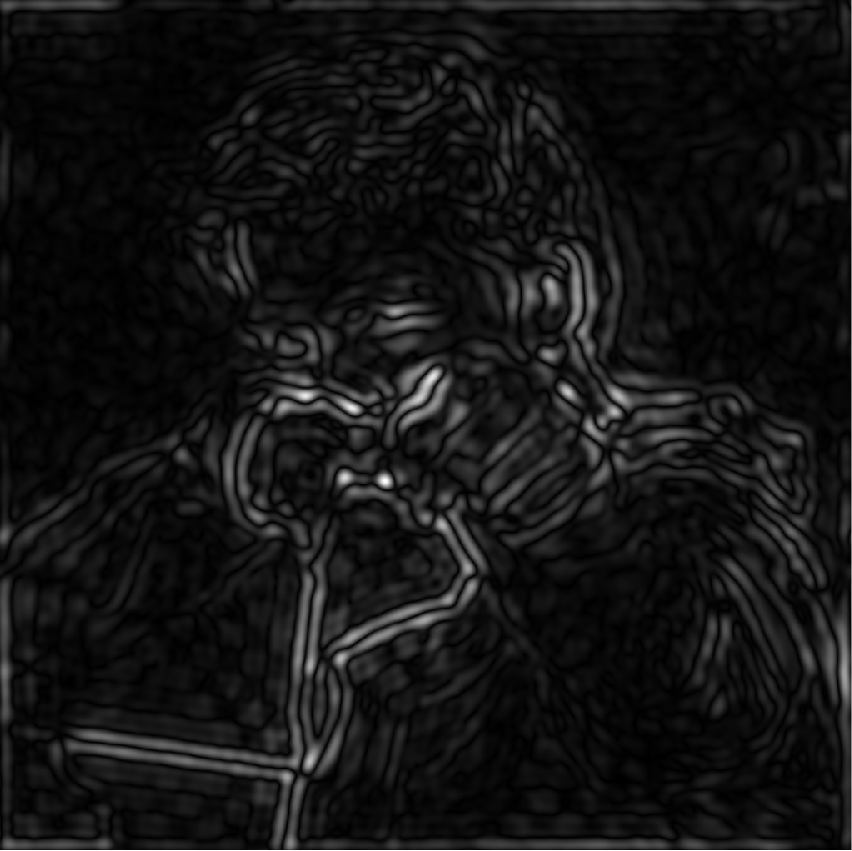
Filter Out High Frequencies (Blur) (滤除高频(模糊))
低通滤波: 只显示低频滤波(画面变模糊,将高频信息盖住)

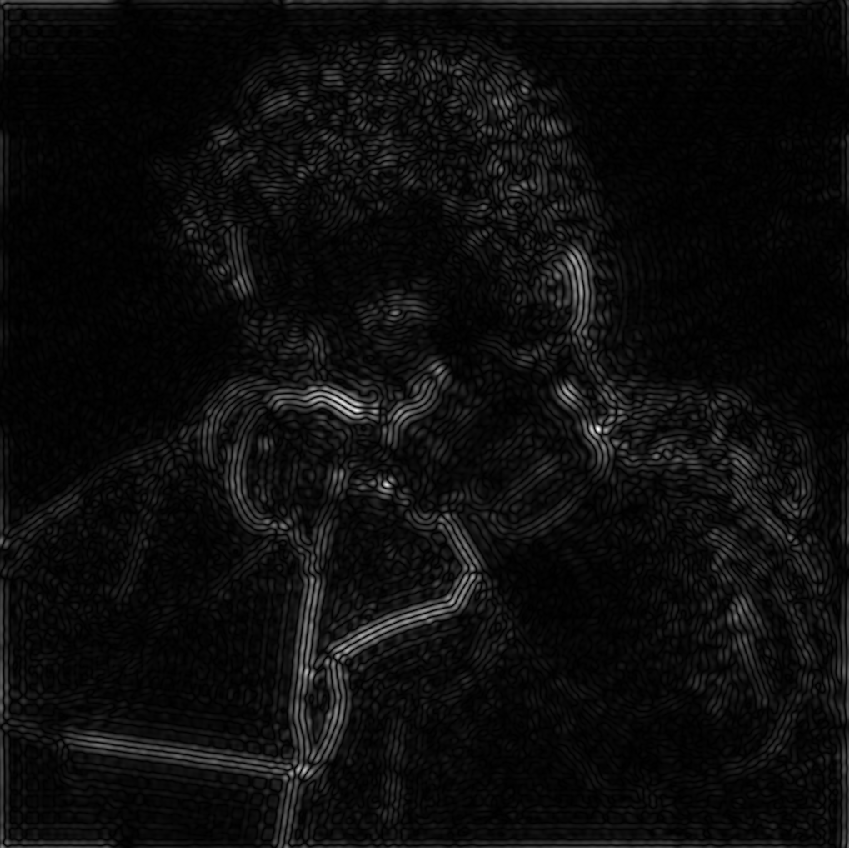
- Filter Out Low and High Frequencies (滤除低频和高频)



Convolution (卷积)
Convolution (卷积)
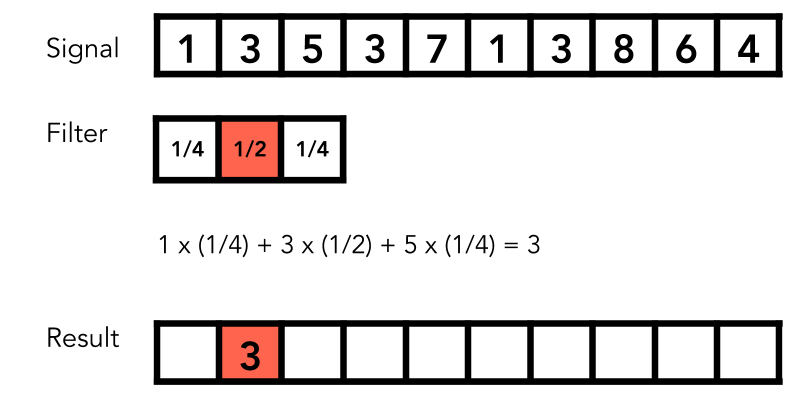
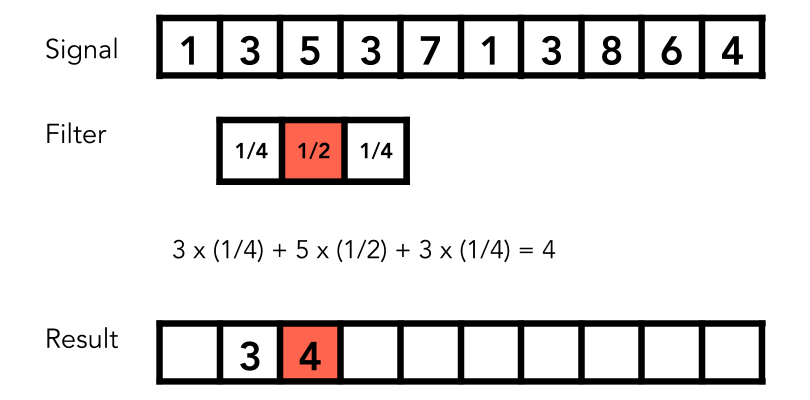
Filtering = Convolution (= Averaging) (滤波=卷积 (=平均))
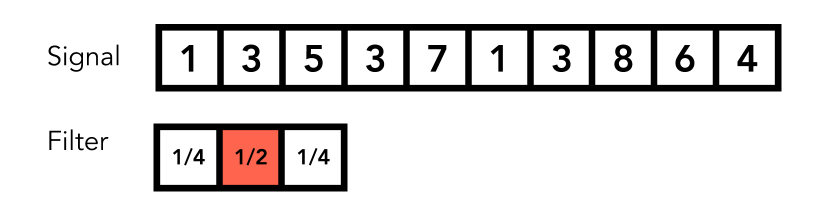
Point-wise local averaging in a “sliding window”(“滑动窗口”中的逐点局部平均)
Convolution Theorem (卷积定理)
简化的定义: 结果为相邻数的平均值
Convolution Theorem: Convolution in the spatial domain is equal to multiplication in the frequency domain, and vice versa (卷积定理): 时域的卷积等于频域的乘积
- Option 1:
- Filter by convolution in the spatial domain (在空间域中通过卷积滤波)
- Option 2:
- Transform to frequency domain (Fourier transform) (变换到频域(傅里叶变换))
- Multiply by Fourier transform of convolution kernel (乘以卷积核的傅里叶变换)
- Transform back to spatial domain (inverse Fourier) (变换回空间域(傅里叶反变换))
- Option 1:
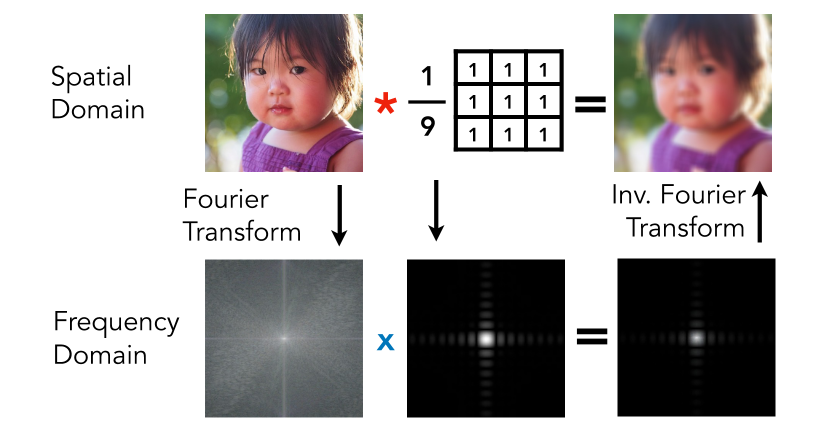
Box Filter
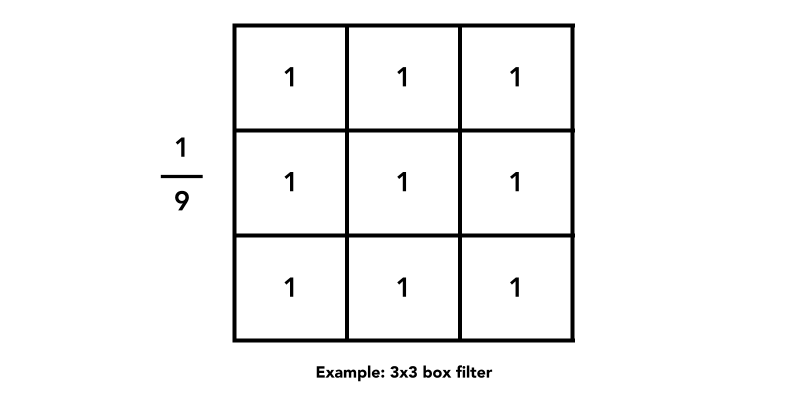
- Box Function = “Low Pass” Filter
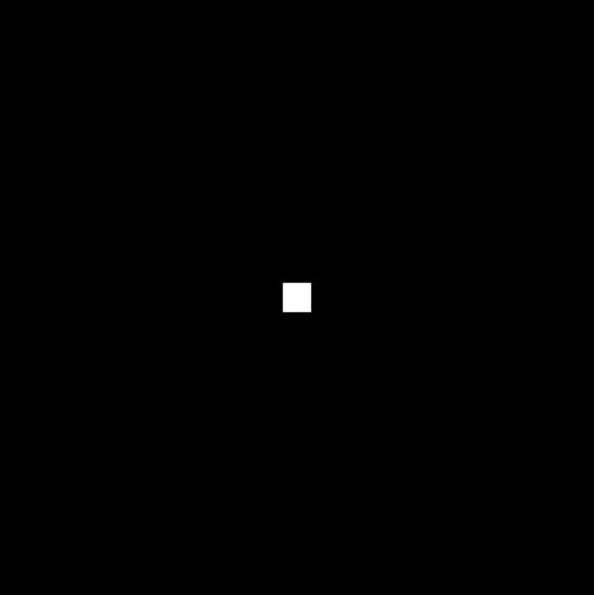

- Wider Filter Kernel = Lower Frequencies
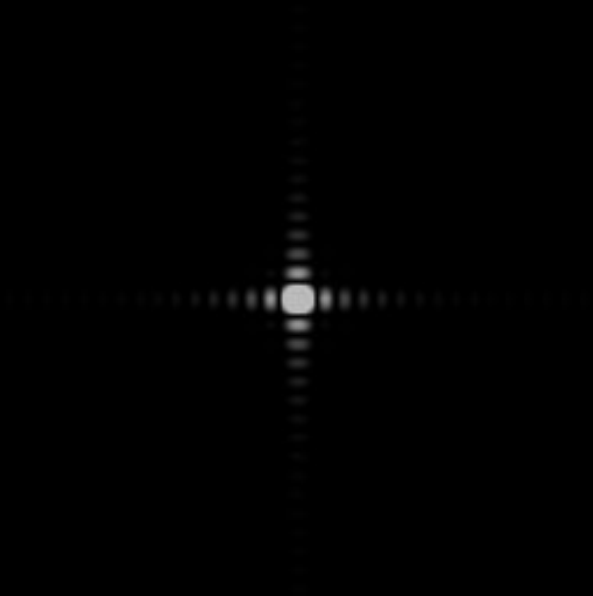

来源及解决
INFO
Sampling = Repeating Frequency Contents (采样=重复频率内容)
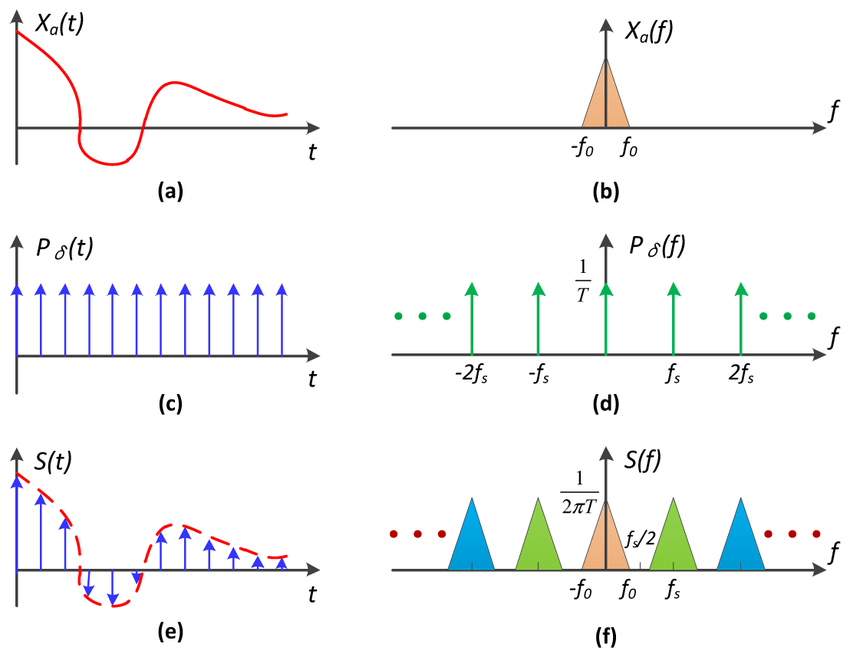
Aliasing = Mixed Frequency Contents (混叠=混合频率内容)
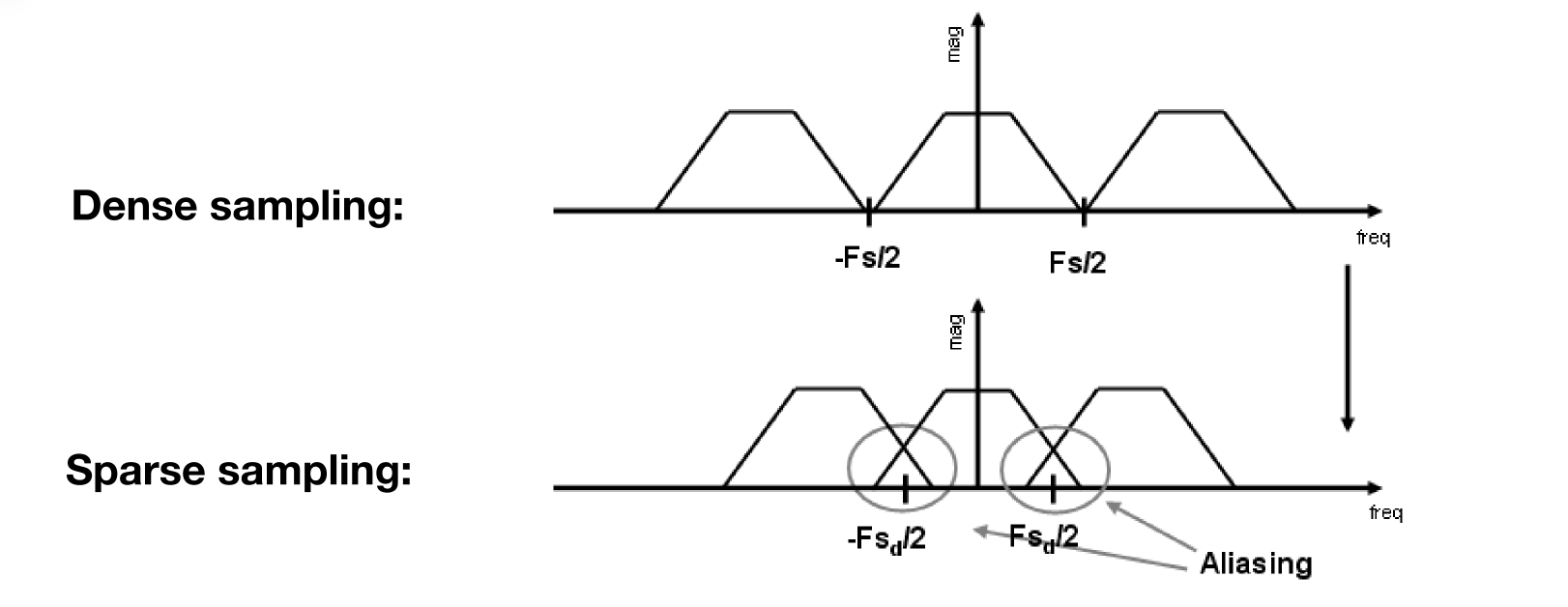
由于采样稀疏,因此出现频谱混叠从而出现锯齿(走样)如果屏幕中像素非常多,密集的采样就不容易出现走样。
因此使用分辨率高的显示器,频谱的搬移间隔大,不容易出现频谱混叠。
TIP
How Can We Reduce Aliasing Error?
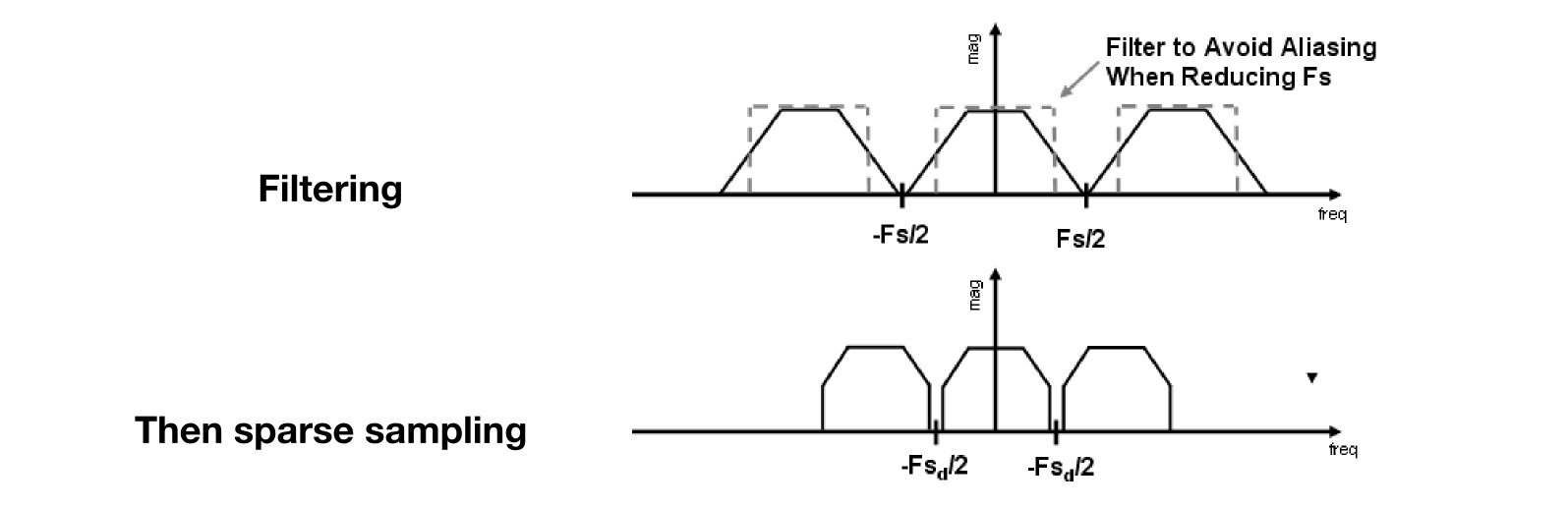
- Option 1: Increase sampling rate (提高采样率)
- Essentially increasing the distance between replicas in the Fourier domain (本质上是增加了傅立叶域中副本之间的距离)
- Higher resolution displays, sensors, framebuffers… (更高分辨率的显示器、传感器、帧缓冲区……)
- But: costly & may need very high resolution (但是:昂贵并且可能需要非常高的分辨率)
- Option 2: Antialiasing (反走样)
- Making Fourier contents “narrower” before repeating (在重复之前使傅里叶内容“更窄”)
- i.e. Filtering out high frequencies before sampling (即: 在采样前滤除高频)
- Option 1: Increase sampling rate (提高采样率)
Regular Sampling (常规取样)
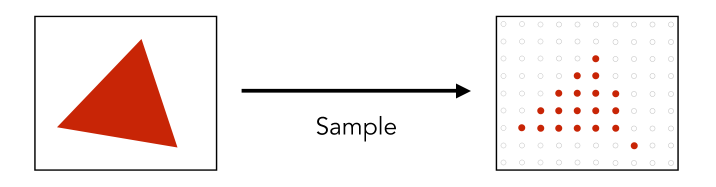
Antialiased Sampling (反走样采样)
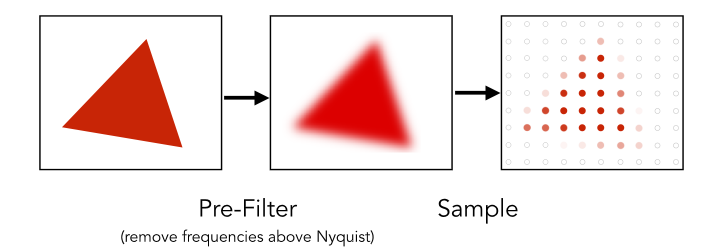
Antialiasing By Averaging Values in Pixel Area (通过在像素区域的平均值来反走样)
- Solution:
- Convolve f(x,y) by a 1-pixel box-blur (对f(x,y)进行1像素的框模糊卷积)
- Recall: convolving = filtering = averaging (卷积=滤波=平均)
- Then sample at every pixel’s center (然后再对每个像素的中心取样)
- Convolve f(x,y) by a 1-pixel box-blur (对f(x,y)进行1像素的框模糊卷积)
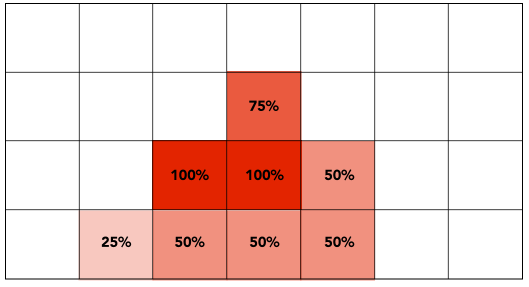
In rasterizing one triangle, the average value inside a pixel area of f(x,y) = inside(triangle,x,y) is equal to the area of the pixel covered by the triangle. (在光栅化一个三角形时,f(x,y) = inside(triangle,x,y)在像素区域内的平均值等于该三角形所覆盖的像素面积。)
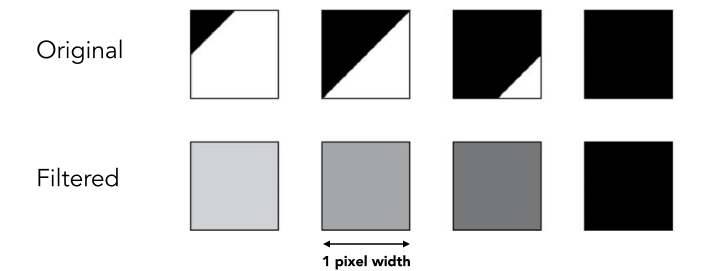
- Solution:
Antialiasing By Supersampling (MSAA) (通过超采样抗锯齿 (MSAA))
MSAA: Antialiasing By Supersampling
Approximate the effect of the 1-pixel box filter by sampling multiple locations within a pixel and averaging their values (通过采样一个像素内的多个位置并取其值的平均值来近似1像素盒滤波器的效果)
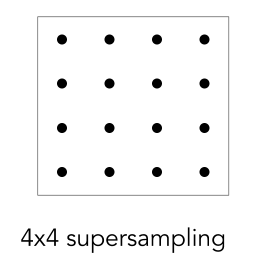
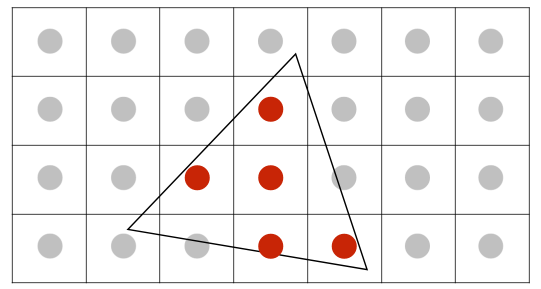
- Supersampling: Step 1 Take NxN samples in each pixel.
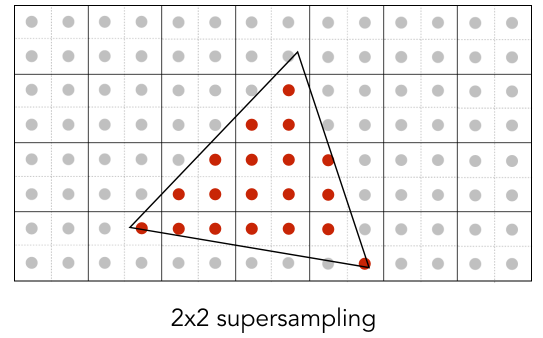
- Supersampling: Step 2 Average the NxN samples “inside” each pixel.
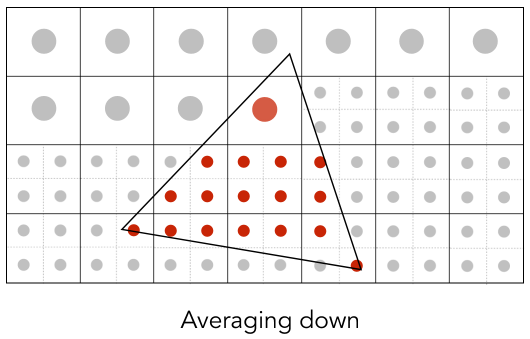
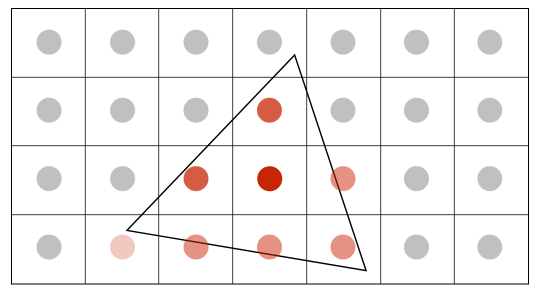
- Supersampling: Result This is the corresponding signal emitted by the display
- Supersampling: Step 1 Take NxN samples in each pixel.
结尾
What’s the cost of MSAA?
增加了很多的计算量
其他的抗锯齿方法
- FXAA (Fast Approximate AA)
- TAA (Temporal AA)
Super resolution / super sampling (Super resolution / super sampling)
- From low resolution to high resolution (从低分辨率处理成高分辨率)
- Essentially still “not enough samples” problem (本质上仍然是“样本不足”的问题)
- DLSS (Deep Learning Super Sampling) (目前可使用DLSS进行超级采样)
Visibility / occlusion (可见性/遮挡)
- Z-buffering (深度缓冲)
Painter’s Algorithm (画家算法)
Inspired by how painters paint Paint from back to front, overwrite in the framebuffer. (灵感来自画家的绘画方式 从后往前涂, 覆盖在帧缓冲区中)
Requires sorting in depth (O(n log n) for n triangles) Can have unresolvable depth order (需要深度排序(O(n log n)对于n个三角形) 会不会有不可解析的深度顺序)
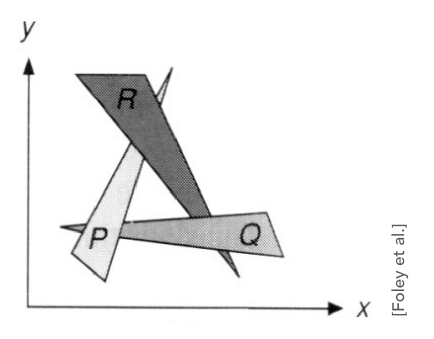
为了解决画家算法的问题, 引入了深度缓冲(Z-Buffer)
Z-Buffer (深度缓冲)
This is the algorithm that eventually won.
- Idea:
- Store current min. z-value for each sample (pixel) (存储当前最小z值为每一个样本(像素))
- Needs an additional buffer for depth values (需要一个额外的深度值缓冲区)
- frame buffer stores color values (帧缓冲区存储颜色值)
- depth buffer (z-buffer) stores depth (深度缓冲区(z-buffer)存储深度)
MPORTANT: For simplicity we suppose z is always positive (smaller z -> closer, larger z -> further) 永远为正(小->近, 大->远)
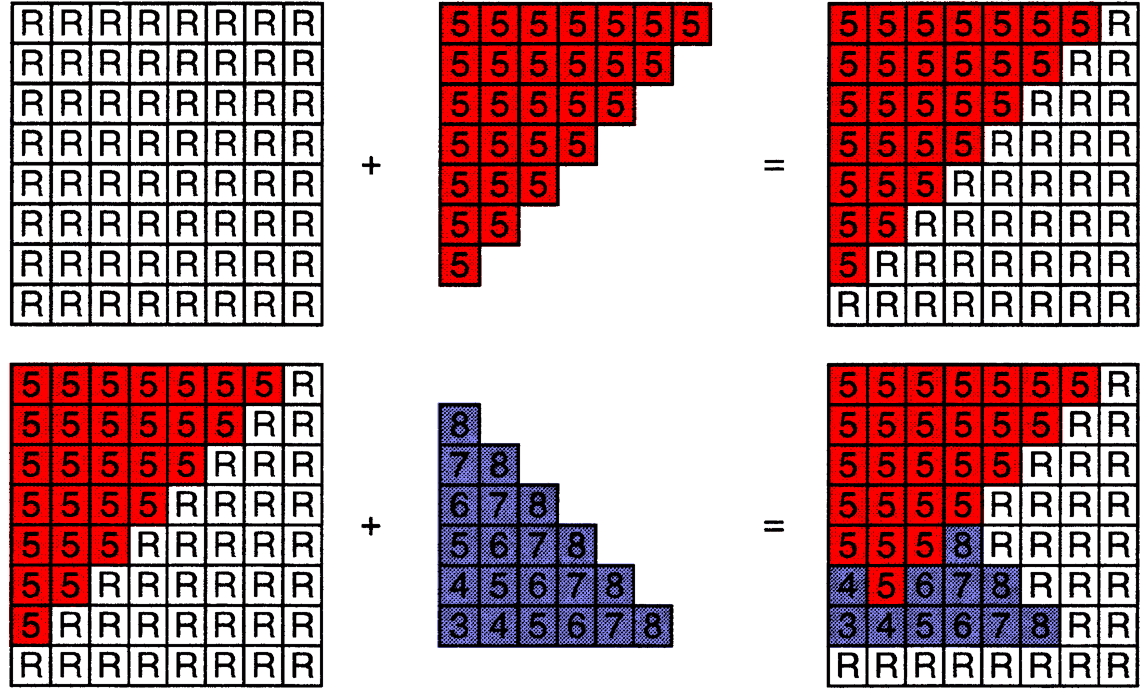
示例:
Code:
//默认深度为无限远
for(each triangle T)
{
for(each sample(x,y,z) in T)//遍历任意一个三角形中的任意一个像素
{
if(z<zbuffer[x,y]) //closest sample so far(目前最接近的样本)
{
framebuffer[x,y] = rgb; //update color
zbuffer[x,y] = z; //update depth
}
else
{
...
}
}
}
Z-Buffer Complexity
Complexity
- O(n) for n triangles (assuming constant coverage)
- How is it possible to sort n triangles in linear time
Drawing triangles in different orders?
Most important visibility algorithm
- Implemented in hardware for all GPUs