几何
这节课
- Introduction to geometry
- Examples of geometry
- Various representations of geometry (几何的各种表示)
Many Ways to Represent Geometry
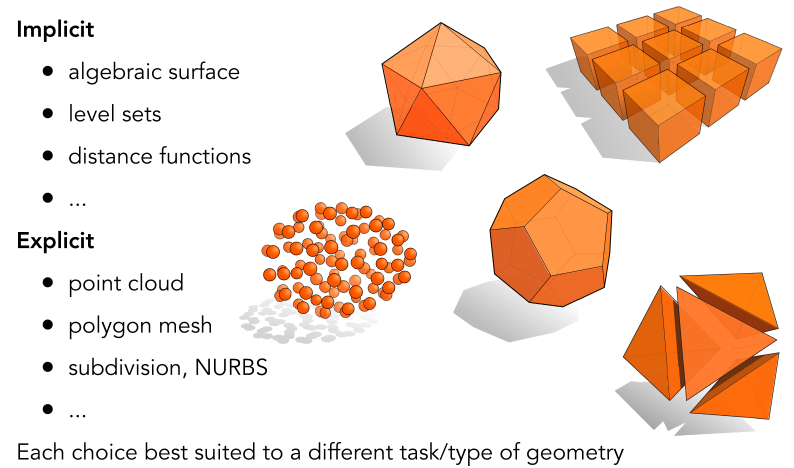
(隐式) Implicit Representations of Geometry
Based on classifying points (基于分类点)
- Points satisfy some specified relationship (点满足某种特定的关系)
E.g. sphere: all points in 3D, where
More generally,
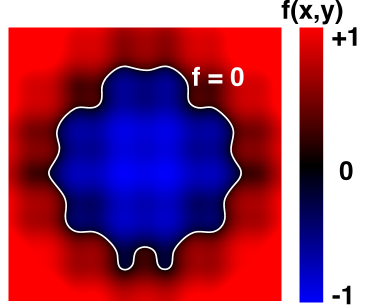
Implicit Surface – Sampling Can Be Hard (隐式表面采样可能很难)

Some tasks are hard with implicit representations (有些任务很难使用隐式表示)
Implicit Surface – Inside/Outside Tests Easy (隐式表面-内部/外部测试容易)
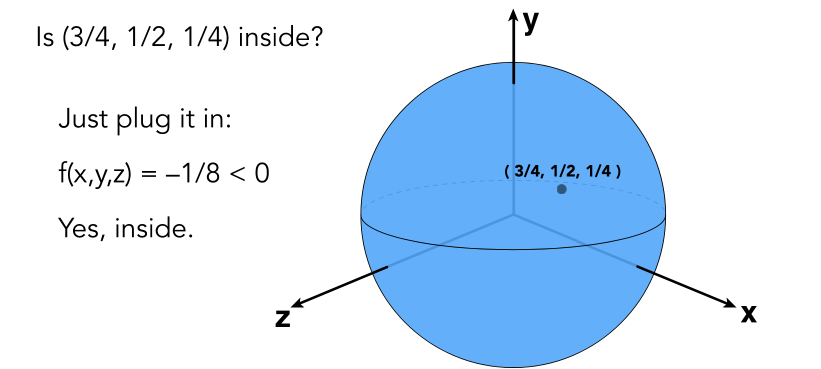
Implicit representations make some tasks easy (隐式表示使一些任务变得容易)
More Implicit Representations in Computer Graphics
Algebraic Surfaces (Implicit) (代数曲面(隐式))
Surface is zero set of a polynomial in x, y, z (曲面是x, y, z的多项式的零集) 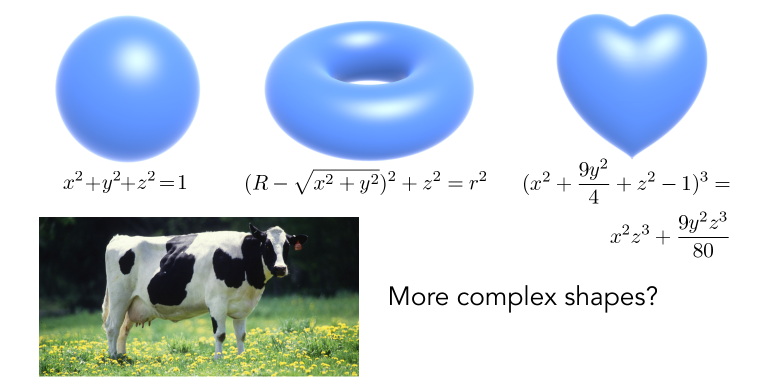
Constructive Solid Geometry (Implicit)
Combine implicit geometry via Boolean operations (复杂的几何体通过简单几何体进行集合运算(交并补)得到,该操作被称之为CSG) 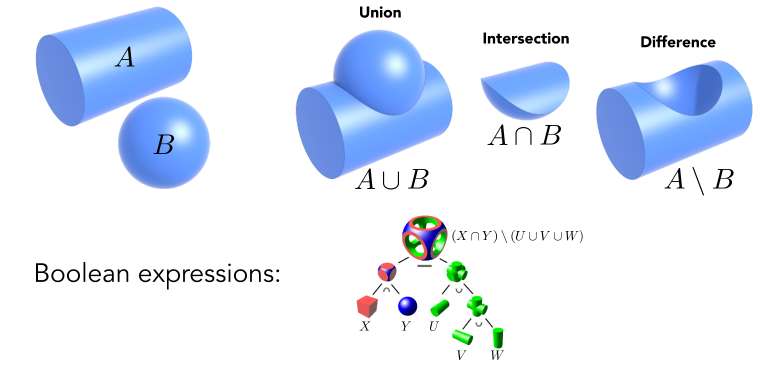
Distance Functions (Implicit) (距离函数)
Instead of Booleans, gradually blend surfaces together using Distance functions: giving minimum distance (could be signed distance) from anywhere to object 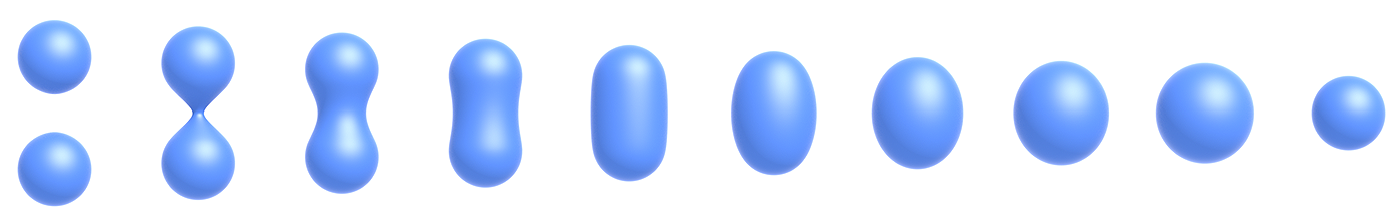
An Example: Blending (linear interp.) a moving boundary (一个例子:混合(线性插值)一个移动的边界) 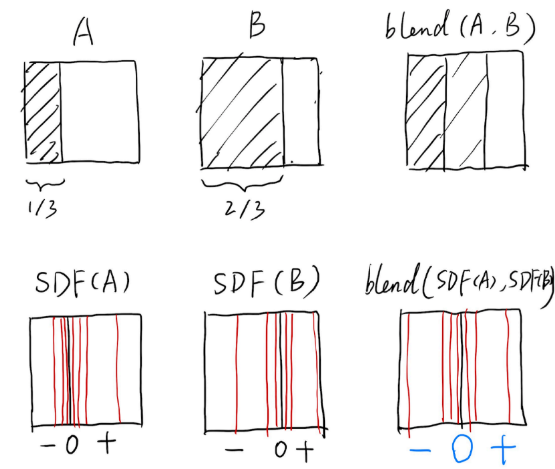
Blending Distance Functions (Implicit)
Can blend any two distance functions d1, d2: 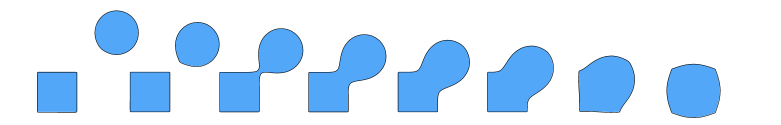
Level Set Methods (Also implicit) (水平集)
Closed-form equations are hard to describe complex shapes Alternative: store a grid of values approximating function (封闭形式的方程很难描述复杂的形状 备选方案:存储一个网格值逼近函数) 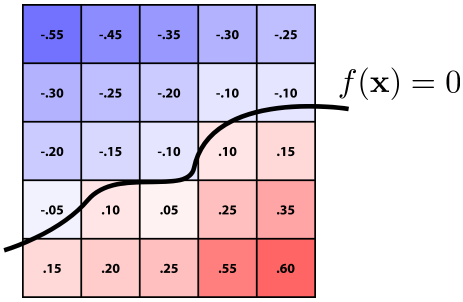 Surface is found where interpolated values equal zero Provides much more explicit control over shape (like a texture) (找到插值值为零的曲面 对形状(如纹理)提供更显式的控制)
Surface is found where interpolated values equal zero Provides much more explicit control over shape (like a texture) (找到插值值为零的曲面 对形状(如纹理)提供更显式的控制)
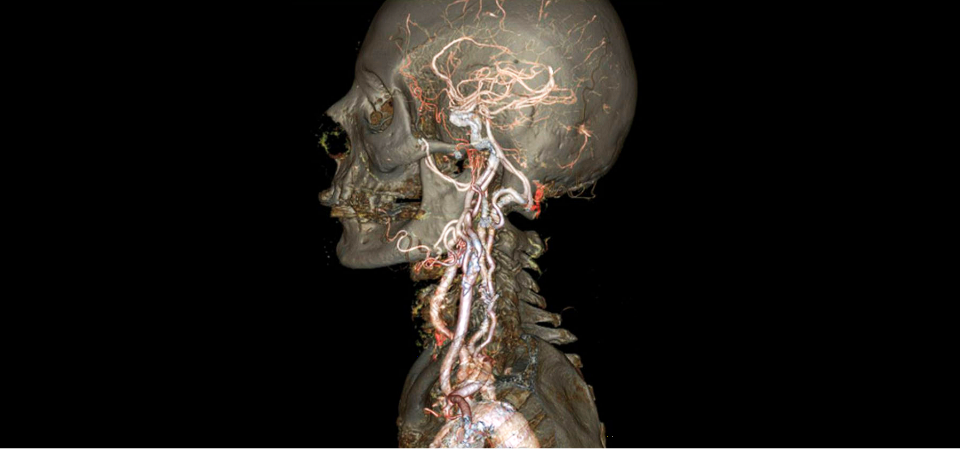
Level Sets from Medical Data (CT, MRI, etc.)
Level sets encode, e.g., constant tissue density
Level Sets in Physical Simulation
Level set encodes distance to air-liquid boundary 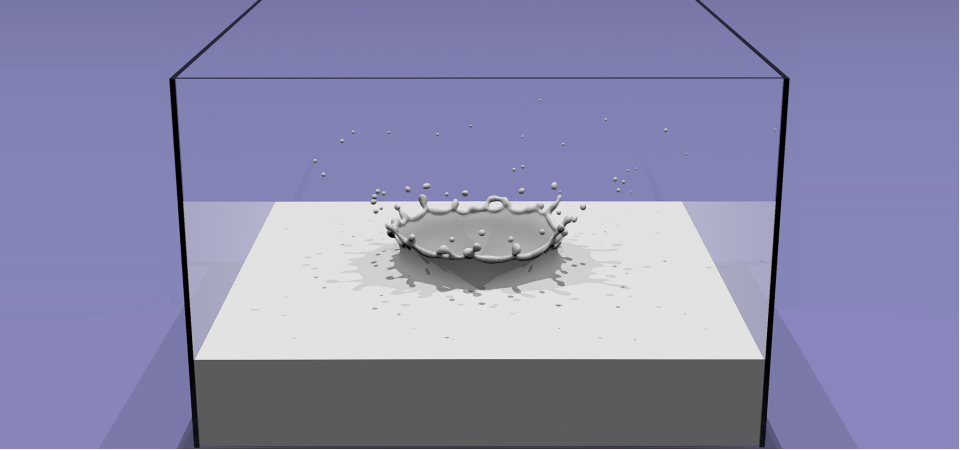
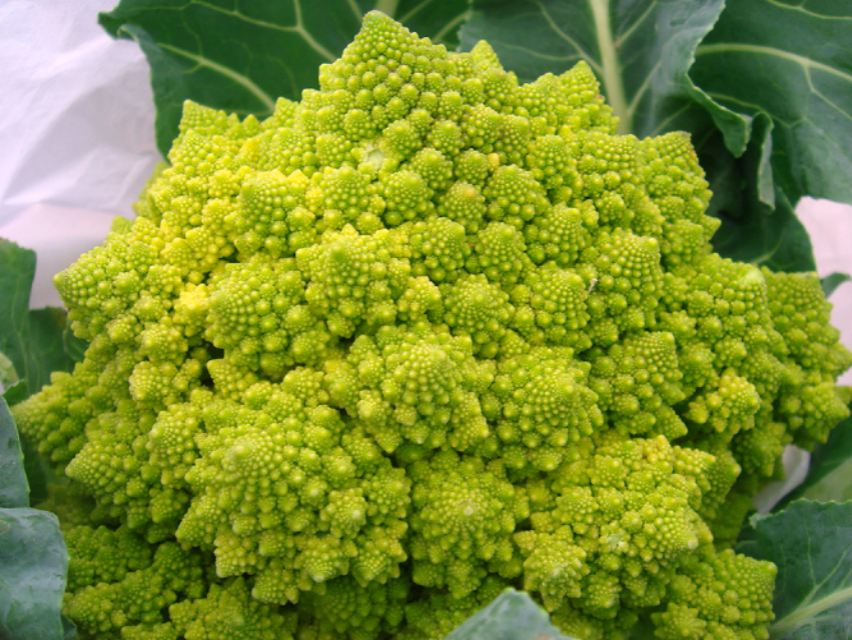
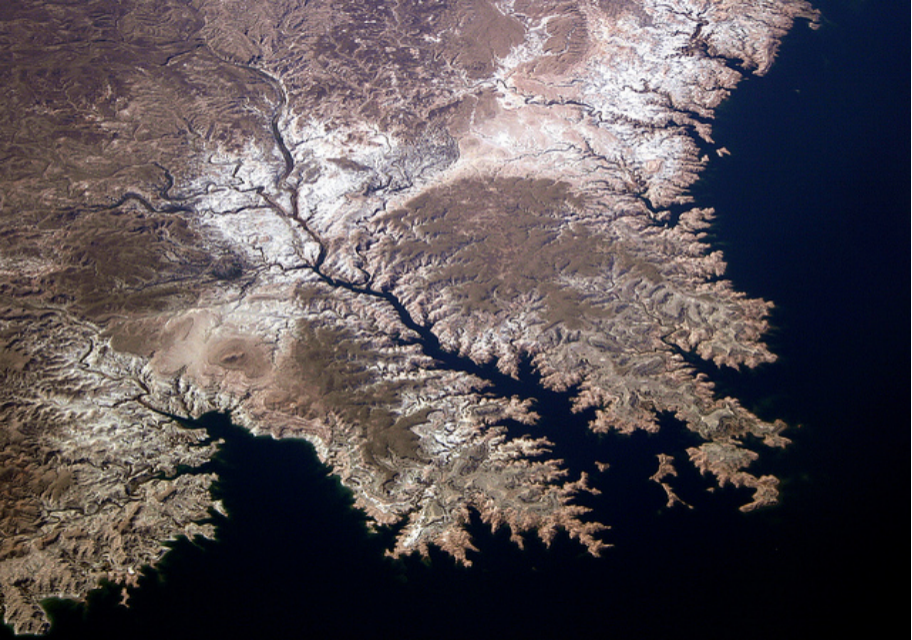
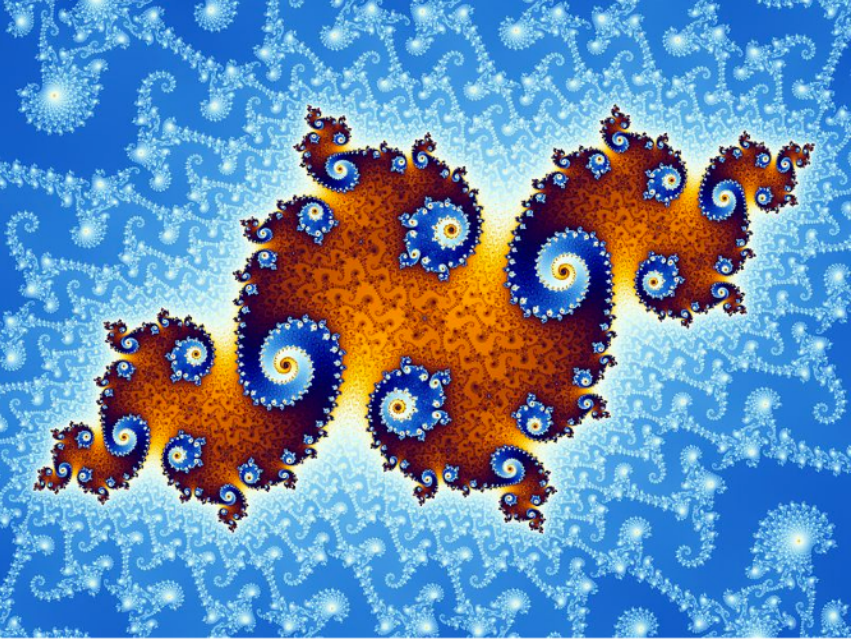
Fractals (Implicit) (分型)
Exhibit self-similarity, detail at all scales
"Language" for describing natural phenomena
Hard to control shape! (展示自相似性,所有尺度的细节 描述自然现象的“语言” 难以控制形状!)


Implicit Representations - Pros & Cons (隐式表示-优点和缺点)
Pros:
- compact description (e.g., a function) (紧凑的描述(例如,一个函数))
- certain queries easy (inside object, distance to surface) (某些查询很容易(对象内部,到表面的距离))
- good for ray-to-surface intersection (more later) (适用于光线与表面的相交)
- for simple shapes, exact description / no sampling error (对于简单的形状,精确的描述/无采样误差)
- easy to handle changes in topology (e.g., fluid) (易于处理拓扑变化(例如,流体))
Cons:
- difficult to model complex shapes (难以模拟复杂的形状)
(显式) Explicit Representations in Computer Graphics
Many Explicit Representations in Graphics
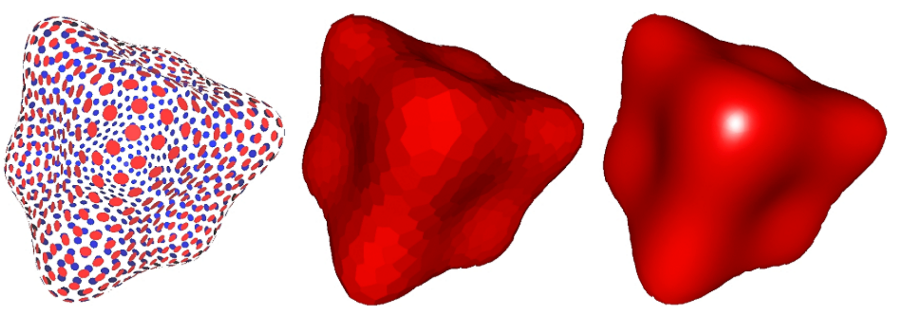
Point Cloud (Explicit) (点云)
Easiest representation: list of points (x,y,z)
Easily represent any kind of geometry
Useful for LARGE datasets (>>1 point/pixel)
Often converted into polygon mesh
Difficult to draw in undersampled regions
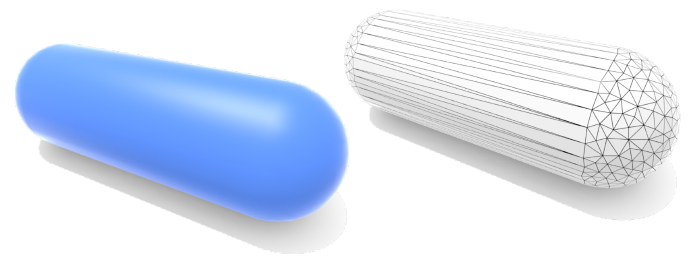
Polygon Mesh (Explicit) (多边形网格)
Store vertices & polygons (often triangles or quads) (存储顶点和多边形(通常是三角形或四边形))
Easier to do processing / simulation, adaptive sampling (更容易做处理/模拟,自适应采样)
More complicated data structures (更复杂的数据结构)
Perhaps most common representation in graphics(也许在图形中应用最广泛)
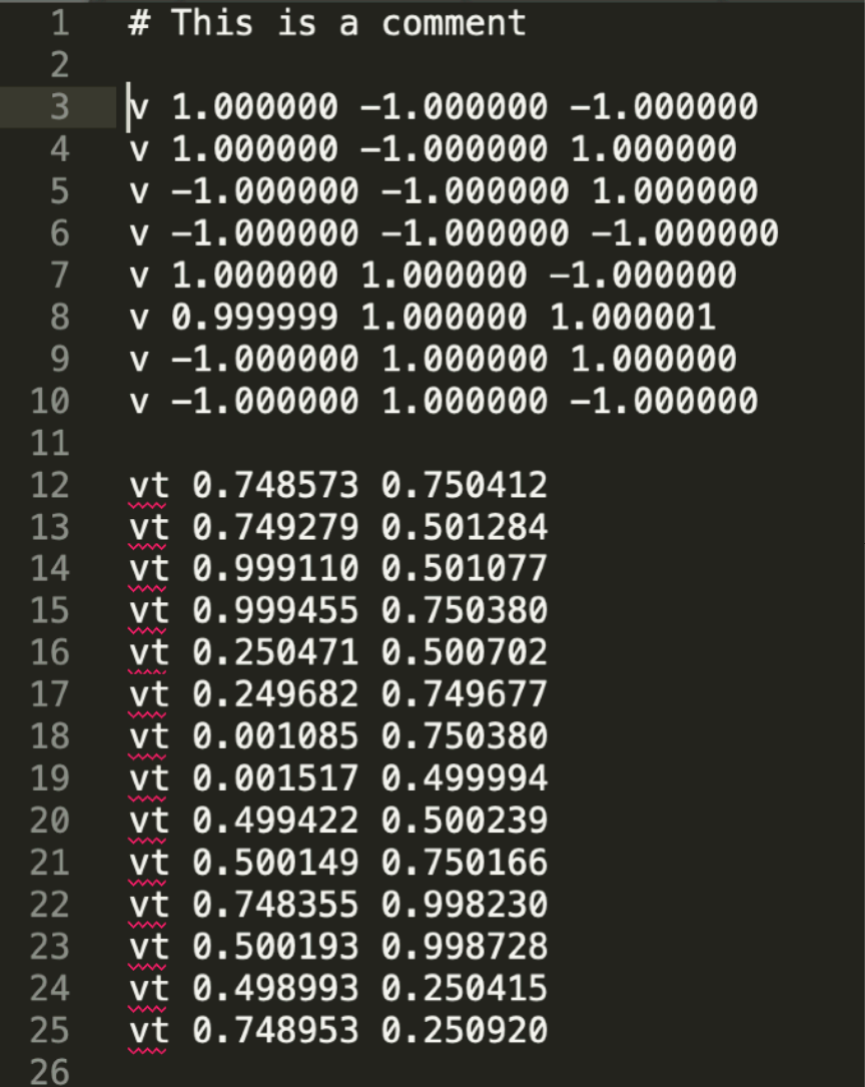
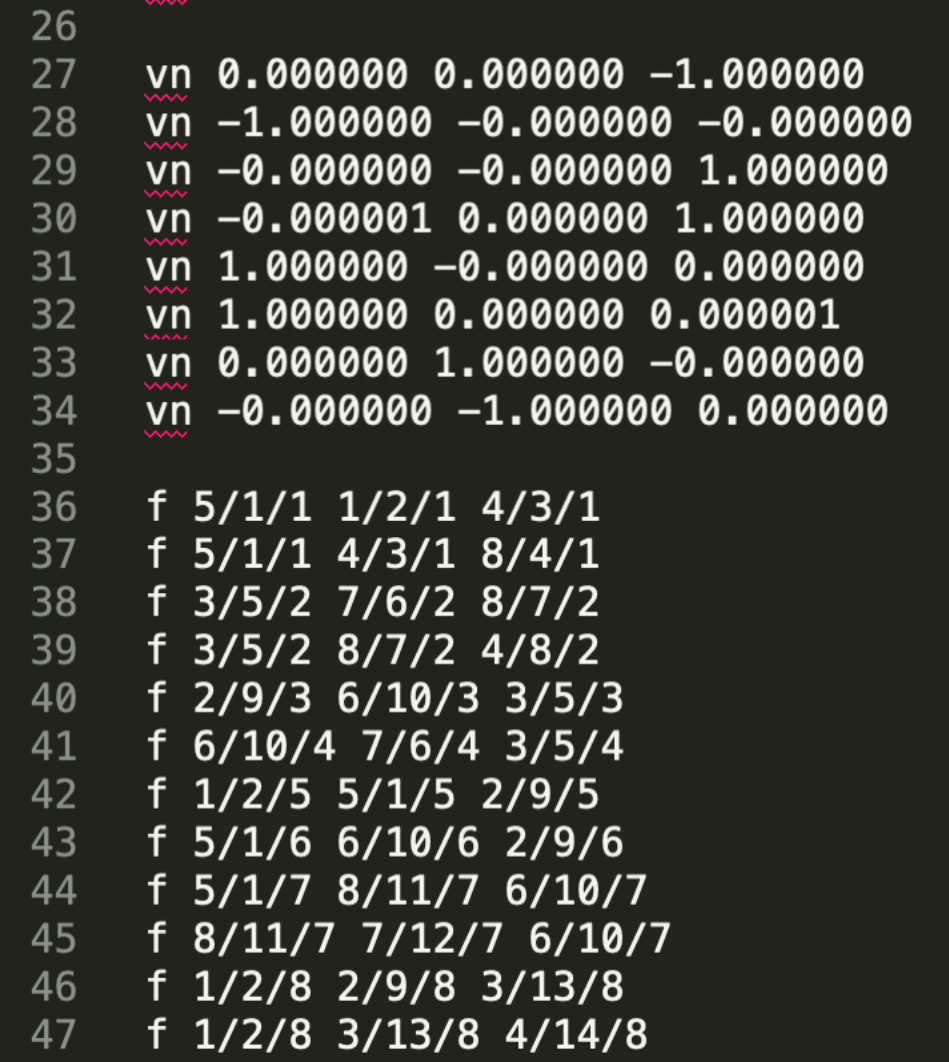
The Wavefront Object File (.obj) Format (波前对象文件(.obj)格式)
Commonly used in Graphics research
Just a text file that specifies vertices, normals, texture coordinates and their connectivities (只是一个文本文件,指定顶点,法线,纹理坐标和它们的连接)
下图定义了一个立方体,有八个顶点(v),六个面(vn)多个纹理坐标(vt)表示,然后使用f表示他们之间的关系(f(v/vt/vn))