Ray Tracing 1 (光线追踪) (Whitted-Style Ray Tracing)
Why Ray Tracing?
Rasterization couldn’t handle global effects well (光栅化不能很好地处理全局效果)
- (Soft) shadows ((软)阴影)
- And especially when the light bounces more than once (尤其是当光线反射不止一次的时候)
- Rasterization is fast, but quality is relatively low (光栅化速度很快,但质量相对较低)
- Ray tracing is accurate, but is very slow (光线追踪是准确的,但速度很慢)
- Rasterization: real-time, ray tracing: offline (光栅化:实时,光线追踪:离线)
- ~10K CPU core hours to render one frame in production
难以将以下效果做好 
Basic Ray-Tracing Algorithm (基本光线追踪算法)
Light Rays (光线)
Three ideas about light rays
- Light travels in straight lines (though this is wrong) (光沿直线传播(虽然这是错误的))
- Light rays do not “collide” with each other if they cross (though this is still wrong) (光线交叉时不会相互“碰撞”(尽管这仍然是错误的)。)
- Light rays travel from the light sources to the eye (but the physics is invariant under path reversal - reciprocity). (光线从光源传播到眼睛(但物理是不变的路径反转-互惠)。)
"And if you gaze long into an abyss, the abyss also gazes into you." — Friedrich Wilhelm Nietzsche (translated) (如果你长时间凝视深渊,深渊也凝视着你。——弗里德里希·威廉·尼采)
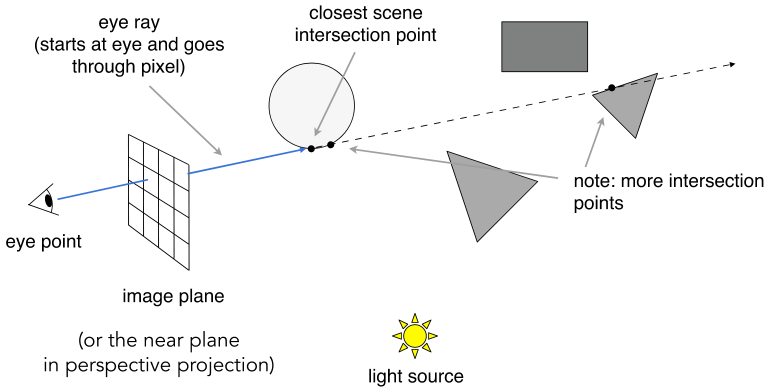
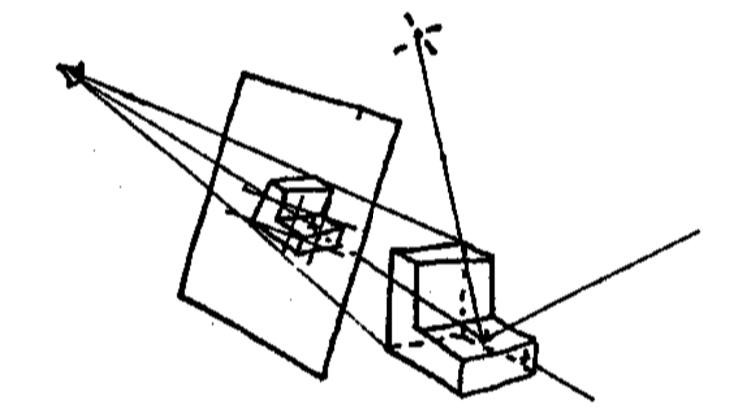
Ray Casting (射线投射)
Appel 1968 - Ray casting
- Generate an image by casting one ray per pixel (通过每个像素投射一条光线来生成图像)
- Check for shadows by sending a ray to the light (通过向光源发送光线来检查阴影)
Ray Casting - Generating Eye Rays
Pinhole Camera Model (针孔相机模型)