几何
关于
- Curves (曲线)
- Bezier Curves (贝塞尔曲线)
- De Casteljau’s algorithm
- B-splines, etc.
- Surfaces
- Bezier surfaces
- Triangles & quads (三角形&四边形)
- Subdivision, simplification, regularization (细分、简化、规范化)
Curves
Bezier Curves (贝塞尔曲线)
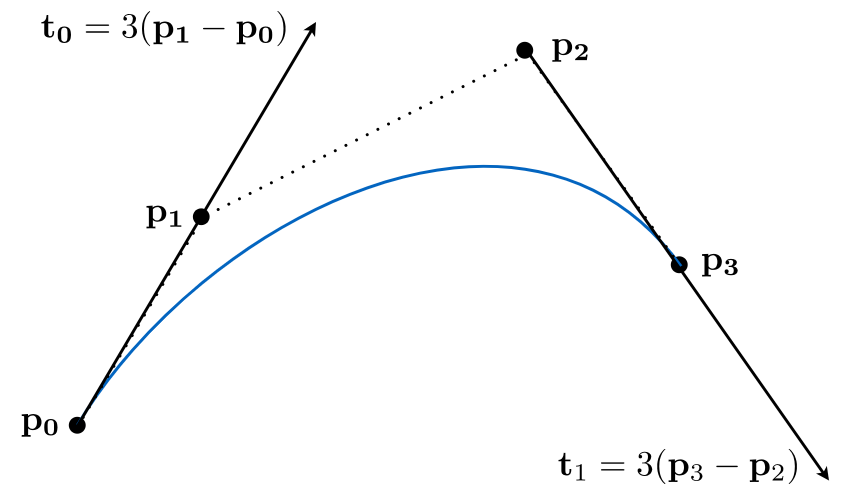
Defining Cubic Bézier Curve With Tangents
只要求一定要经过起止点, 起止点之间的若干个控制点用于控制曲线弯曲的方向, 最终形成一条经过起止点的光滑曲线被成为贝塞尔曲线.
Bézier Curves – de Casteljau Algorithm
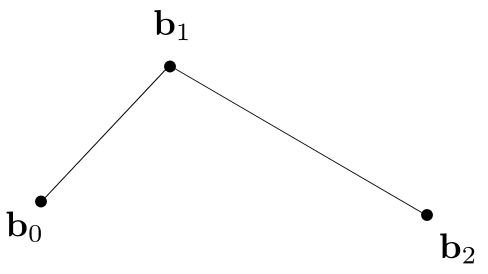
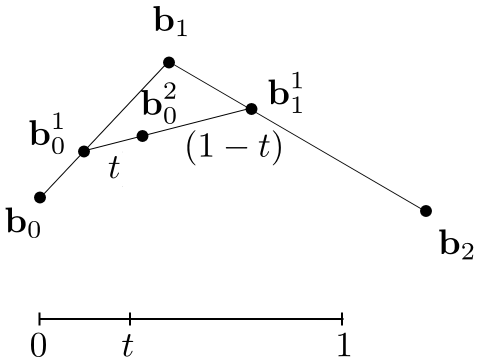
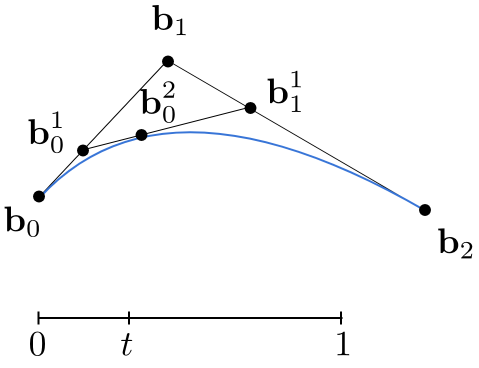
Consider three points (quadratic Bezier) (考虑三个点(二次贝塞尔))
Insert a point using linear interpolation (使用线性插值插入一个点)
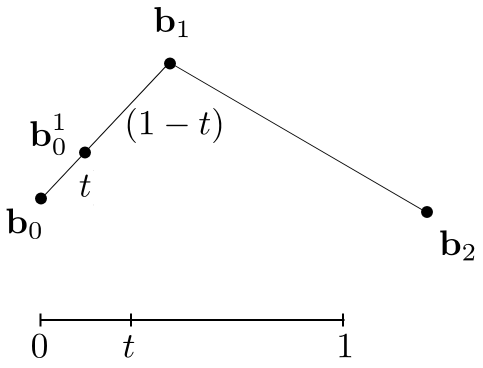
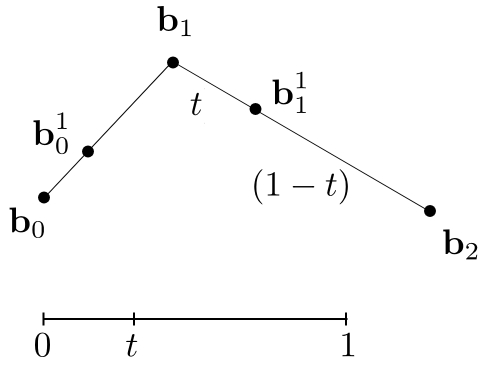
Insert on both edges (两边插入)
Repeat recursively (重复递归)
Run the same algorithm for every t in [0,1] (对[0,1]中的每个t运行相同的算法)
Cubic Bézier Curve – de Casteljau
Four input points in total, Same recursive linear interpolations (总共四个输入点, 同样的递归线性插值) 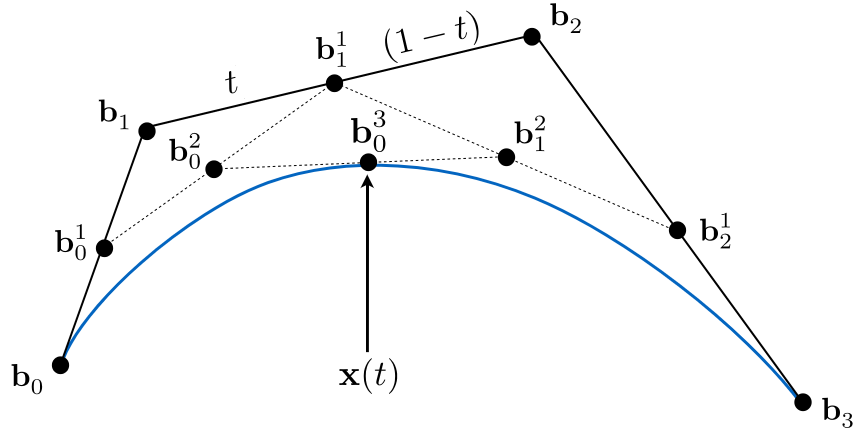
Evaluating Bézier Curves Algebraic Formula (算法评估)
Bézier Curve – Algebraic Formula (公式)
de Casteljau algorithm gives a pyramid of coefficients (给出了系数金字塔?) 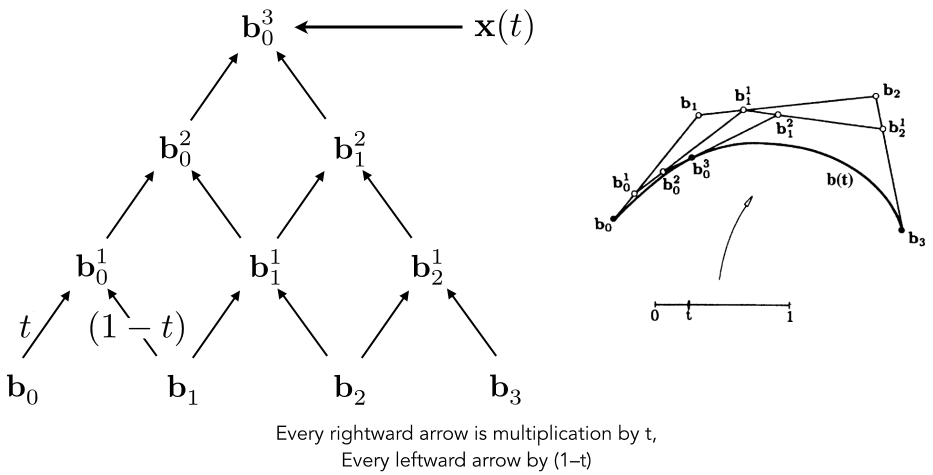
Example: quadratic Bézier curve from three points
- 引入参数t(范围[0, 1])
- 取
到 , 到 上t位置的点 , - 将
, 连接 - 取
到 t位置上的点 - 将[0, 1]上所有的
点都遍历一份相连即可得到贝塞尔曲线 - 若有n个控制点则将上面步骤进下递归操作直到找到最终位移
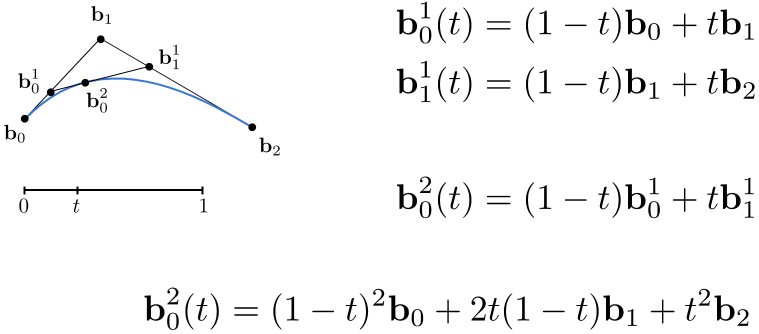
Bernstein form of a Bézier curve of order n: (n阶公式)
求得以t为自变量的函数, 由这些点形成的集合构成贝塞尔曲线.
Bernstein polynomials (伯恩斯坦多项式):
Example: assume n = 3 and we are in R³
i.e. we could have control points in 3D such as:
These points define a Bezier curve in 3D that is a cubic polynomial in t:
- 对贝塞尔曲线做仿射变换只需要对控制点、起止点做仿射变换再重新绘制一遍即可
- 对投影变换没有这样的性质
Convex Hull (凸包)
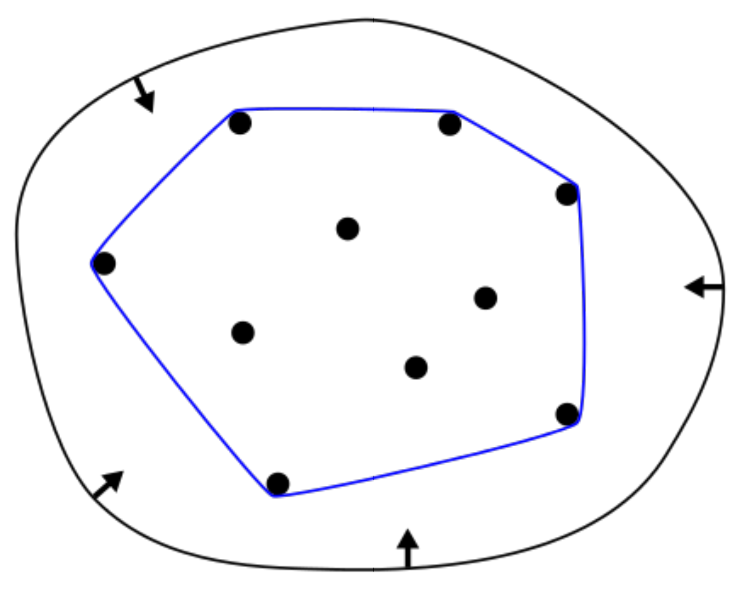
- 贝塞尔曲线拥有凸包的性质
- 连接贝塞尔曲线最外围的控制点, 将其相互连接形成一个封闭空间, 画出来的贝塞尔曲线一定在凸包范围内
- 若贝塞尔曲线是一个直线则凸包也是一个直线
Piecewise Bézier Curves (分段贝塞尔曲线)
高阶贝塞尔曲线难以控制, 不常用. 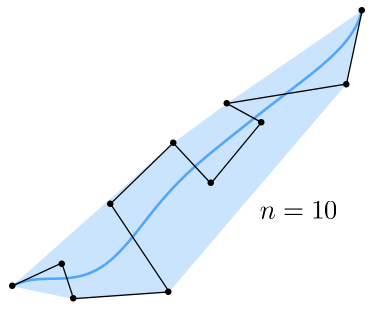
Instead, chain many low-order Bézier curve, Piecewise cubic Bézier the most common technique
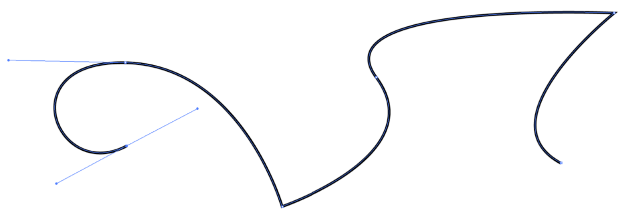
若想要逐段贝塞尔曲线平滑过渡则需要将相邻控制点共线, 否则会出现该曲线后边段的不平滑现象.
Widely used (fonts, paths, Illustrator, Keynote, …) (广泛使用(字体,路径,Illustrator, Keynote,…))
Demo: David Eck, http://math.hws.edu/eck/cs424/notes2013/canvas/bezier.html
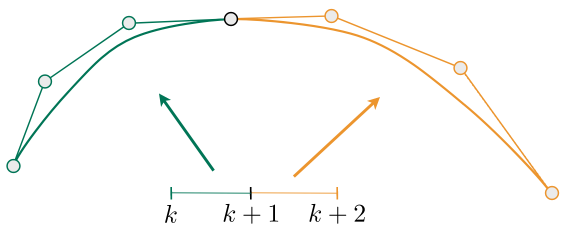
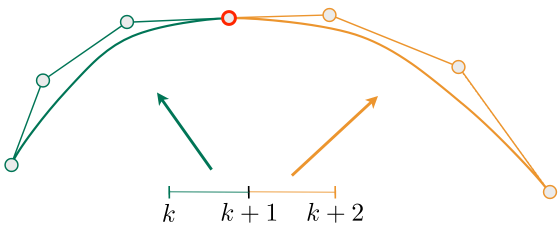
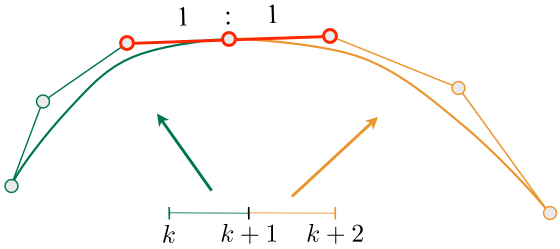
连续
Two Bézier curves
Assuming integer partitions here, can generalize (假设这里是整数分区,可以推广)
Bézier Surfaces
Extend Bézier curves to surfaces (扩展到曲面)
Bicubic Bézier Surface Patch (双立方贝塞尔表面贴片)
Bezier surface and 4 x 4 array of control points 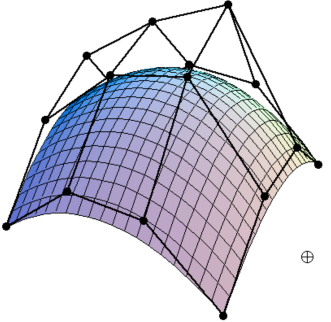
Evaluating Bézier Surfaces (评估)
Evaluating Surface Position For Parameters (u,v) (求参数(u,v)的曲面位置)
For bi-cubic Bezier surface patch,
Input: 4x4 control points
Output is 2D surface parameterized by (u,v) in [0,1]2
(对于双立方贝塞尔曲面贴片,输入:4x4个控制点 输出为2D曲面,参数化为[0,1]2中的(u,v)) 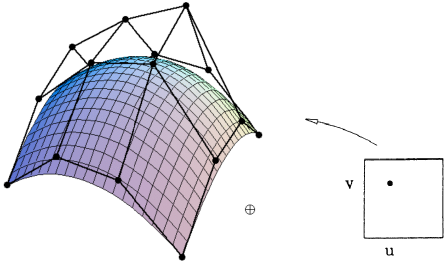
Method: Separable 1D de Casteljau Algorithm
Goal: Evaluate surface position corresponding to (u,v)
(u,v)-separable application of de Casteljau algorithm
- Use de Casteljau to evaluate point u on each of the 4 Bezier curves in u. This gives 4 control points for the “moving” Bezier curve
- Use 1D de Casteljau to evaluate point v on the “moving” curve
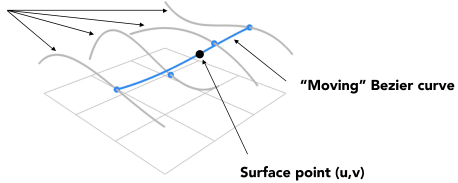
懒得翻译了, 大概思路就是: 与二维的贝塞尔曲线思想类似, 但是需要定义两个参数u和v(取代之前的参数t)
先对f(u)进行遍历得到曲线,再嵌套遍历得到曲面f(u, v), 类似于两层for循环进行遍历.